Fig. 2. FS binding site in mammalian AC.
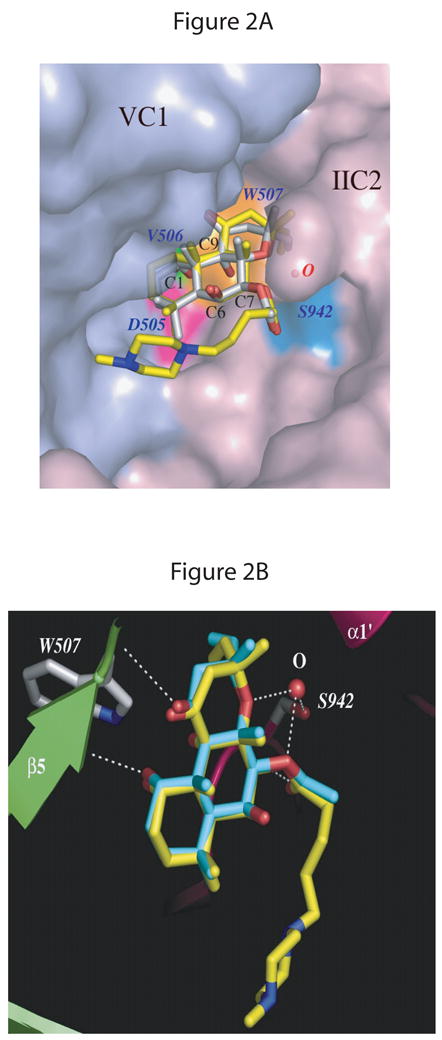
The AC structure with DMB-FS (PDB: 1AZS) is superimposed on both C1 and C2 domains of the AC structure with FS (PDB:1CS4). A, overview. The molecular surface of the VC1 and IIC2 proteins in the diterpene binding pocket is displayed in light-blue and light-pink, respectively. FS and DMB-FS are drawn as stick models; carbon atoms are gray for FS and yellow for DMB-FS, nitrogens blue, and oxygens red. Three conserved residues from VC1 forming a binding pocket in proximity to the C1-OH group of FS/DMB-FS are colored magenta for Asp505, green for Val506, and orange for Trp507. A water molecule bridges the side chain of Ser942 (cyan) from IIC2 and two oxygens of the FS/DMB-FS. B, detail view. VC1 and IIC2 are shown in lime and pink, respectively. Secondary structure elements are labeled as defined previously [12]. FS and DMB-FS are drawn as stick models; carbon atoms are cyan for FS, yellow for DMB-FS and gray for side chains of protein residues, nitrogens blue, and oxygens red. The white dashed lines depict the hydrogen bonds between amino acid residues Val506 of VC1 and C1-OH of FS, Ser942 (IIC2) and C7-OH of FS via a water molecule as well as Ser508 (VC1) and C11-OH of FS. Fig. 2 was generated using the PyMol program (DeLano Scientific, San Carlos, CA, USA).
