Figure 2. AQP2 transgenic mouse models of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
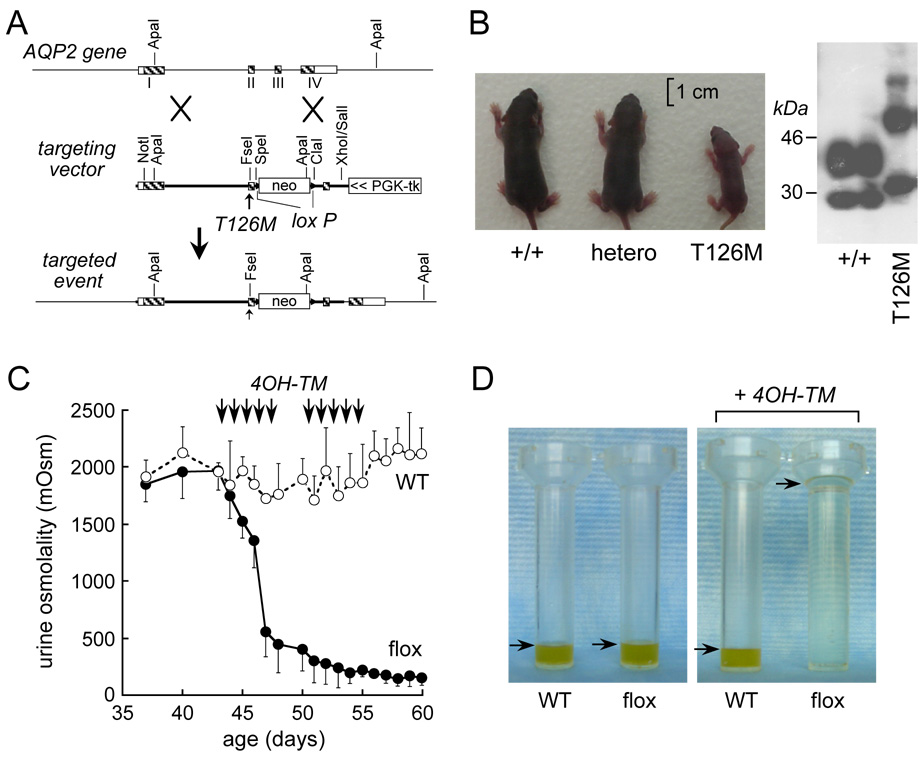
A. Targeting strategy for introduction of the T126M mutation into AQP2 gene replacement. Homologous recombination results in replacement of the indicated segment (thick line) of the AQP2 gene by a 1.8-kb neomycin selection cassette flanked by loxP sites. B. (left) Photograph of mice of indicated genotypes at 5 days after birth. (right) Immunoblot of kidney homogenates. C. Urine osmolality in tamoxifen-treated wildtype mice (open circles) and AQP2flox mice (filled circles) given free access to food and water (S.E.). Arrows indicate tamoxifen injections. D. Twenty-four hour urine output in untreated (left) and tamoxifen-treated (right) WT and AQP2flox mice (arrows indicate urine level). Adapted from refs. 27, 28.
