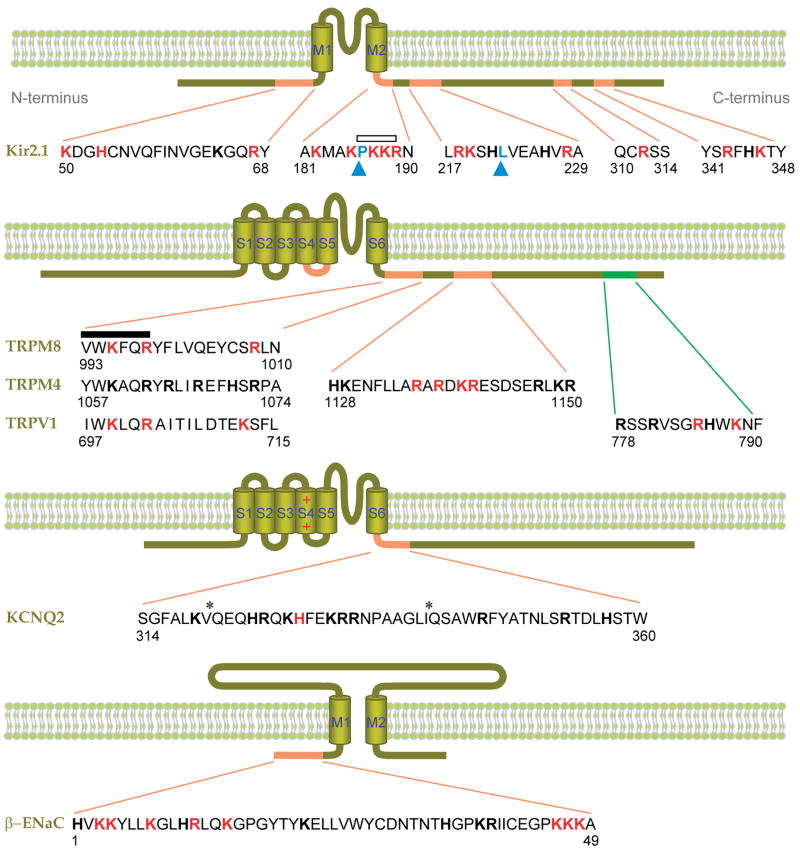
Figure 5.
Putative PIP2-interacting residues of ion channels. Shown are Kir2.1 (32, 45), β-ENaC (48, 94), KCNQ2 (95), and several TRP channels (5, 54, 69, 64). Basic amino acids experimentally implicated in PIP2 binding are red, and other basic residues are shown in block bold. Hydrophobic residues implicated in PIP2 binding are indicated by blue arrowheads (76, 96). The distal C-terminal sequence of TRPV1 implicated in inhibition by PIP2 is green (64). Asterisks denote putative calmodulin binding sites. An open bar indicates a conserved PKKR domain in Kir channels involved in PIP2 binding, and the closed bar indicates the highly conserved TRP box (XWK(F/X)QR). Numbers indicate the amino acid positions. M1–2 and S1–6 denote the transmembrane domains.