Fig. 5.
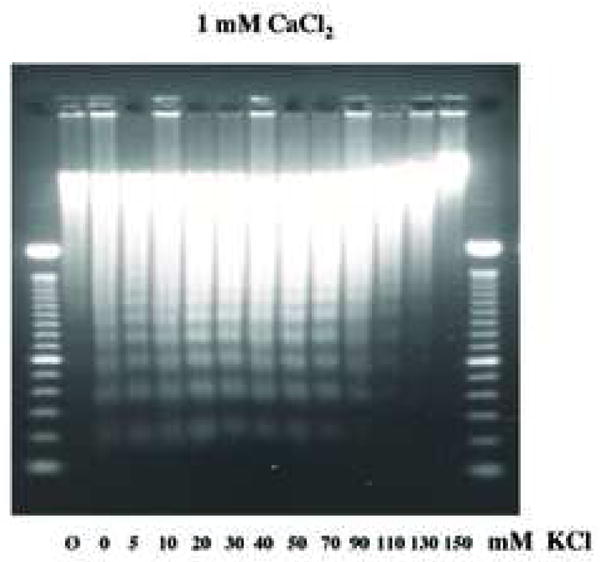
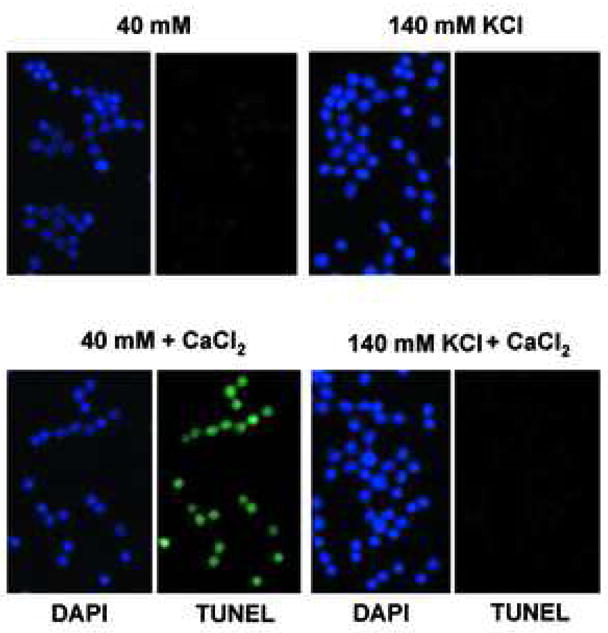

Physiological concentration of K+ blocks Ca2+-dependent DNA degradation in nuclei. (a) TUNEL assay, Nuclei (1 × 104) were incubated under “apoptotic” (40 mM) and “physiological” concentration (140 mM) of K+ with 1 mM CaCl2. Right, fluorescent TUNEL assay. Left, counter staining with DAP I. The data shown represents at least three experiments. (b) Analysis of Ca2+-dependent DNA degradation under various concentration of K+. DNA was extracted and run on agarose gel electrophoresis. Nuclei (2 × 106) were incubated with 1 mM CaCl2 together with an increasing concentration of KCl. For each sample, 1 μg of DNA was analyzed. “Ø” denotes control nuclei maintained on ice. The data shown represents one of three independent experiments.
