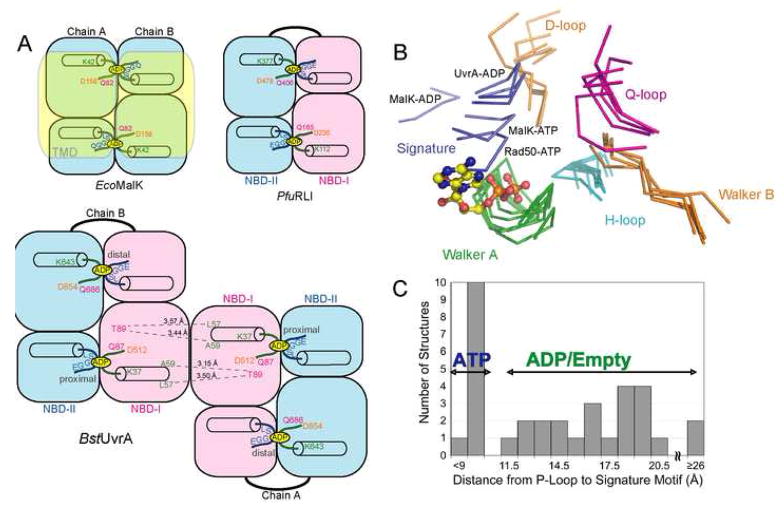
Figure 2.
Structural comparison of the NBDs of BstUvrA and other ABC ATPases. The conserved ATPase motifs are colored as follows: Walker A/P-loop, green; Walker B and D-loop, orange; ABC signature motif, blue; Q-loop, magenta; and H-loop/switch, cyan. (A) Arrangement of the NBDs in E. coli MalK, Pyrococcus furiosus RNaseL inhibitor (RLI), and BstUvrA. Key residues important for nucleotide binding and interactions across the dimer interface are shown. The transmembrane portion of MalK is depicted in transparent yellow. (B) NBDs of UvrA were superimposed with the NBDs of the maltose transporter MalK (ADP-bound, PDB code 2AWO; ATP-bound, PDB code 1Q12), and Rad50 (ATP-bound, PDB code 1F2U) using their respective ATP-binding domains. All the motifs are from the same NBD except for the ABC signature motif and the D-loop, which are part of the opposing NBD. The bound ADP is from the proximal site of UvrA protomer A and is represented as ball-and-stick. (C) Histogram showing the distance between the Cα atoms of the conserved Lys residue in the Walker A motif and Ser residue in the ABC signature motif in the structures of ABC ATPases solved in the dimeric state (PDB codes 2R6F, 2AWO, 1Q1B, 1Q1E, 2AWN, 1YQT, 1L7V, 2ONK, 1Q12, 1F2U, 1XEF, 1XEX). Asterisk denotes the average distance for the four nucleotide-binding sites in UvrA.