Figure 6. Lovastatin inhibited TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in ARPE-19 cells.
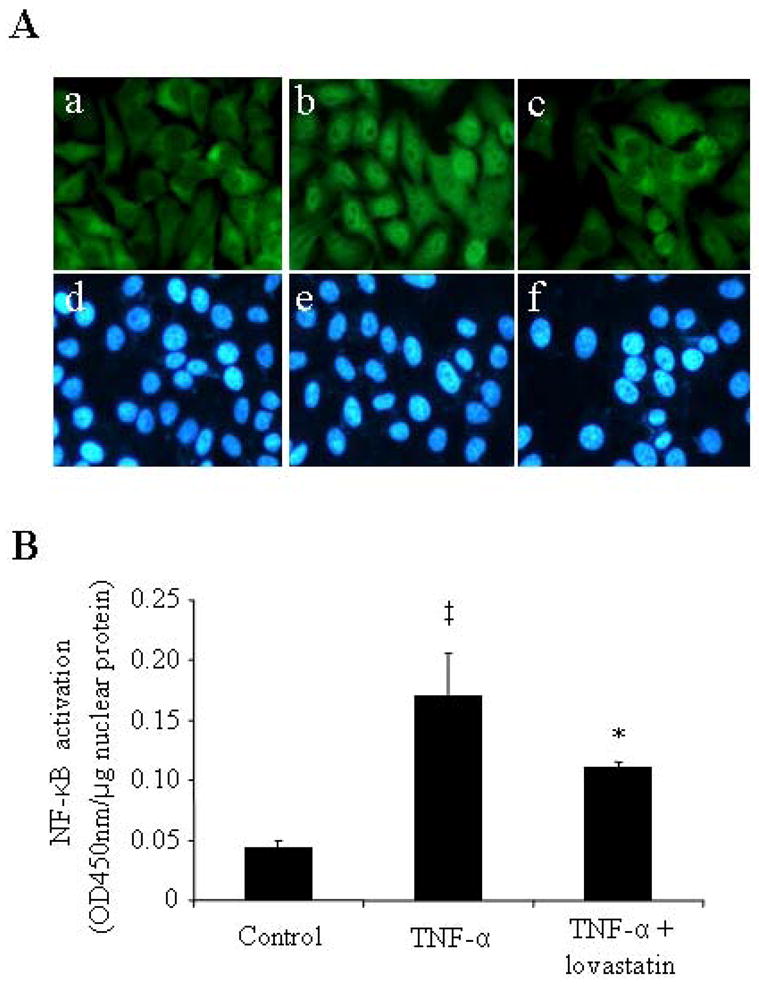
Sub-confluent ARPE-19 cells were pre-incubated in the absence or presence 1 μM lovastatin for 24 h before the treatment with or without TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 1 h. A: Cells were fixed and stained by an anti-NF-κB antibody and visualized under a fluorescent microscope. Magnification: 400×. a–c: NF-κB staining; d–e: nuclear staining. Note that the signal of NF-κB was diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm in untreated control cells (A-a), and translocated from the cytoplasm to the nuclei in the cells exposed to TNF-α (A-b), which was effectively blocked by lovastatin (A-c). B: Transcriptional activity of NF-κB in the nuclear extract of ARPE-19 cells was quantified by TransAM™ NF-κB p65 transcription factor assay. Results were presented as mean ± SD (n=3). The values statistically different from control cells were indicated by ‡ P<0.01; from TNF-α-treated cells were indicated by *P<0.05.
