Fig. 11.
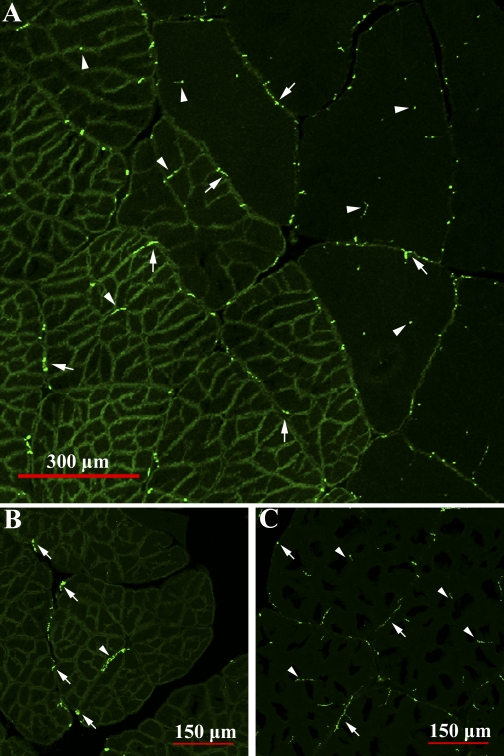
Muscle cross sections labeled with anti-SYNORF1, an antibody to the presynaptic vesicle-associated phosphoprotein synapsin, that reveal innervation patterns in light and dark levator fibers. For emphasis, labeling is shown in the transition zone of light and dark fibers (A) and in light (B) and dark (C) fibers independently. Inherent autofluorescent properties of the sarcolemma make the fiber boundaries visible. In both fiber types, synapses were visualized at the fiber sarcolemma (arrows) and inside the fiber core (within sarcolemmal clefts) and between subdivisions (arrowheads). Synapse density is not higher in dark fibers (left in A) than in light fibers (right in A), which would be expected if subdivisions were independent contractile units.