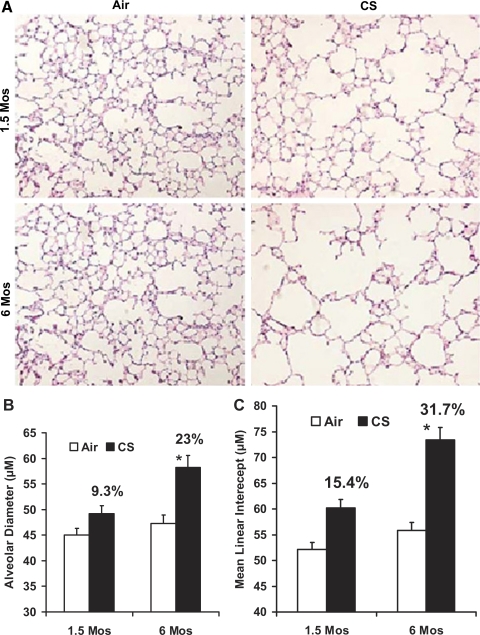
Fig. 1.
Increased air space enlargement in A/J mice exposed to chronic cigarette smoke (CS). A: H&E-stained lung sections from A/J mice exposed to room air or CS at the indicated time points. Lung sections from the 6-mo CS-exposed mice show increased alveolar destruction and air space enlargement compared with the lung sections from age-matched air-exposed A/J mice. Sections from the age-matched air-exposed mice show normal alveolar structure (n = 5 mice/group); original magnification, ×20. The images (15 fields/slide) of the H&E-stained lung sections from the air- and CS-exposed mice were acquired with a Nikon E800 microscope, and alveolar diameter (B) and mean linear intercepts (C) were determined by computer-assisted morphometry with the Image Pro Plus software. Six-month CS-exposed A/J mice show a significantly increased alveolar diameter (B) and mean linear intercept (C) compared with 1.5-mo CS-exposed mice. Data are means ± SE. *P ≤ 0.05.