Figure 3. PTK/ZK activates ERK in vivo.
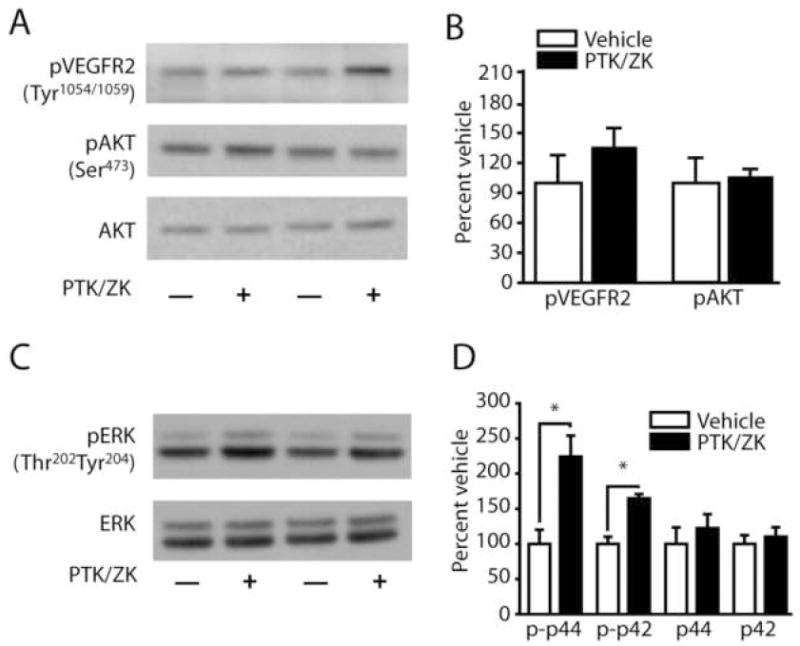
A) Representative western blots showing VEGFR2 (Tyr1054/1059) and AKT (Ser473) phosphorylation following intrahippocampal infusion of 1μl of either 5μM PTK/787 or vehicle. B) Summary results showing that PTK/ZK does not significantly alter VEGF or AKT phosphorylation in vivo. C) Representative western blots showing ERK (Thr202Tyr204) phosphorylation following intrahippocampal infusion of 1μl of either 5μM PTK/787 or vehicle. D) Summary results showing that intrahippocampal infusion of PTK/ZK significantly increases phospho-ERK (both p44 and p42) immunoreactivity compared to the vehicle-infused contralateral hippocampus. No change was observed in total ERK levels. p-p42, phospho-p42 ERK; p-p44, phosphor-p44 ERK; *, P ≤ 0.05 by two-tailed t-test.
