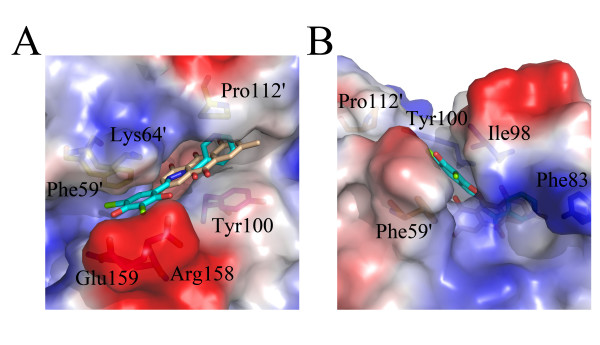
Figure 5.
The structure superposition diagram of Emodin and compound 1 in models A and B. The electrostatic surface of the active tunnel is rendered by a color ramp from red to blue. Emodin, compound 1 and surrounding critical residues are shown as sticks and colored wheat, cyan, yellow (for monomer A), magenta (for monomer B), blue (for monomer C) and orange (for monomer D), respectively. Bromine on the compound 1 is colored green. (A) Emodin are located near the entrance of the active tunnel and stacked between Tyr100 and Pro112' in model A. The pyridine ring of compound 1 is also sandwiched as Emodin, while the 2,4-dihydroxy-3,5-dibromo phenyl ring at the other end of compound 1 stretches into another pocket formed by Arg158, Glu159, Phe59', Lys62' through hydrophobic interactions. (B) Emodin and compound 1 are located near the catalytic site of the active tunnel in model B. Emodin extents to the bottom of the tunnel and is located in the hydrophobic pocket. The pyridine ring of compound 1 adopts a similar conformation with Emodin. While the 2,4-dihydroxy-3,5-dibromo phenyl ring at the other end of compound 1 stretches out of the tunnel forming a sandwich conformation with residues Ile98 and Phe59' via π-π interactions.