Figure 3.
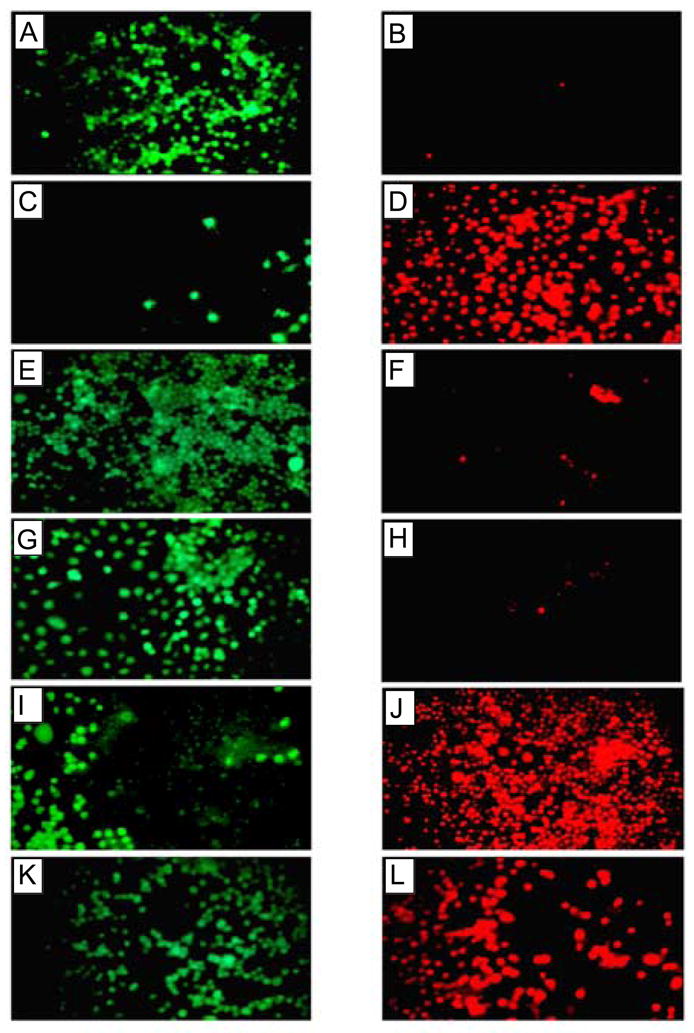
Cell viability assay of neuronal cells treated with Aβ(1–42). Cellular toxicity induced by Aβ(1–42) was blocked by Zn2+ and by removal of extracellular calcium, but not by tachykinin or NMDA antagonist. Fluorescence images of cells treated with calcein (live cells, left panels) and ethidium homodimer 1 (dead cells, right panels) are shown after Aβ(1–42) treatment. Panels A and B show control cells not treated with Aβ(1–42), panels C and D show cells treated with 10 μM Aβ(1–42), panels E and F show cells after Aβ(1–42) treatment in the absence of extracellular calcium, panels G and H show cells after Aβ(1–42) treatment in the presence of 50 μM ZnCl2, panels I and J show cells after Aβ(1–42) treatment in the presence of 20 μM tachykinin (physalaemin), and K and L show cells after Aβ(1–42) treatment in the presence of 20 μM MK-801, an NMDA receptor antagonist [11].
