Figure 1.
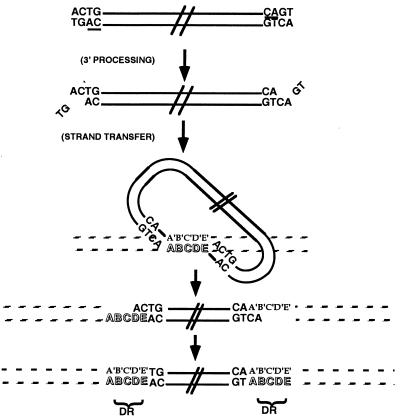
HIV-1 IN activities. A schematic diagram of HIV-1 IN activities depicts the double-stranded DNA viral genome at the top as parallel black lines with the terminal nucleotides CAGT. The conserved 3′ CA dinucleotide is underlined at each viral end. IN first acts in the cytoplasm to remove the two 3′ nucleotides (3′ processing), leaving a 2-nt overhang at each 5′ end. In the nucleus, IN mediates a concerted integration (strand transfer) by ligating each 3′ end of the viral DNA (looped structure) to the host DNA (striped lines). This generates a “gapped intermediate” with free viral 5′ ends that are repaired to generate the fully integrated provirus. The characteristic HIV-1 5-bp staggered strand transfer is depicted by the letters A-E in the target DNA, and the resulting 5-bp direct repeats (DR) of host DNA flanking the provirus are indicated.