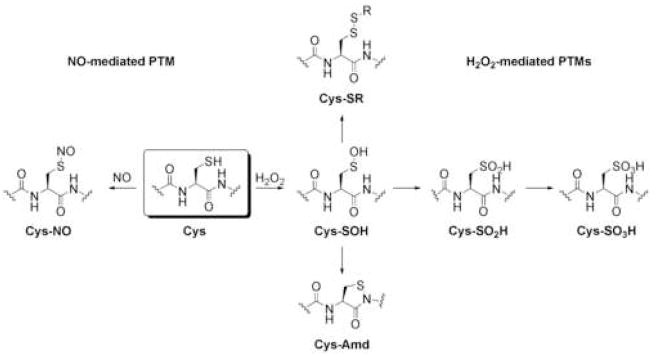
Figure 1.
Oxidative PTMs of cysteine. Oxidation of cysteine residues by H2O2 results in the formation of cysteine sulfenic acids (Cys-SOH) that can be subsequently trapped in a variety of ways. Reactions with intra- or intermolecular thiols can form disulfides, ultimately leading back to the cysteine sulfhydryl. Further oxidation results in formation of cysteine sulfinic (Cys-SO2H) and sulfonic acids (Cys-SO3H), respectively. Intramolecular capture of Cys-SOH with the nitrogen atom of the neighboring amide backbone forms the intriguing cyclic sulfenyl amide (Cys-Amd).