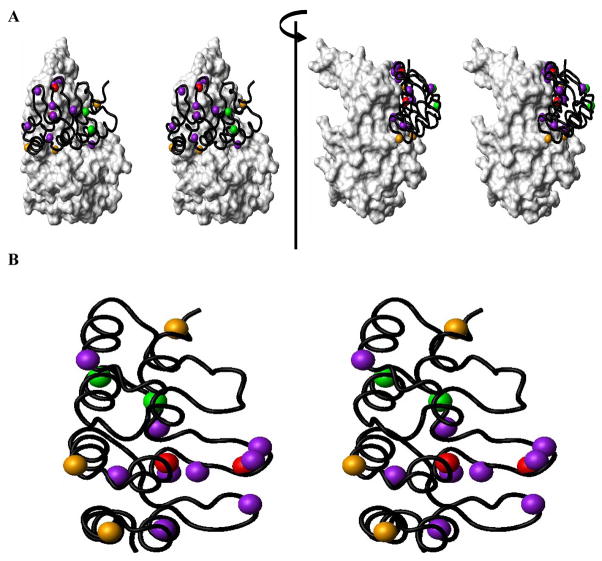
Figure 1. Structural Basis of p16/CDK6 (or CDK4) Interaction.
(A) Structural positioning of the functionally important residues of P16 in contact with CDK6 is shown using the crystal structure of the P16/CDK6 complex15 (PDB code: 1BI7). (B) Quantitative contributions of functionally important residues of P16. Residues are presented in different colors based on changes in the values of IC50 when mutated16, 17. Residues with >20 fold increase in IC50 when mutated are indicated in red (L78 and D84); 10–20 fold, orange (W15, D92 and R124); 5–10 fold, green (H66 and E69), and 3–5 fold, purple (E26, N71, P76, A77, T80, H83, F90, W110, and L121).