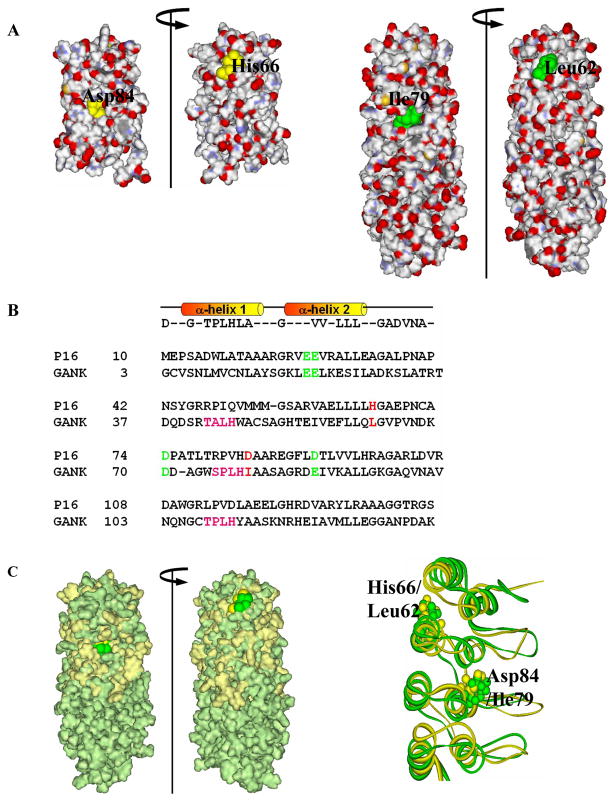
Figure 2. Structure-based sequence homology between P16 and gankyrin.
(A) Surface charge distribution of P16 (PDB ID: 1DC2; left) and gankyrin (PDB ID: 1TR4; right) indicating the location of the two residues of interest. (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of human P16 and the first four ARs of gankyrin. Four negatively charged CDK4-binding residues, E28, E29, D74, and D92 of P16 (highlighted in green) are conserved in gankyrin as E20, E21, D70, and E87, respectively (green). Two residues of interest, H66 and D84 of P16, and corresponding gankyrin residues L62 and I79, are highlighted in red. (C) Surface-fitted overlay of P16 and gankyrin (left) and the ribbon drawing of best fit superimposition of the backbone (N, Cα, and C) atoms of the NMR structures of P16 (gold) and the first four ankyrin repeats of gankyrin (green). Two residues of interest, H66 and D84 of P16 (gold) as well as their corresponding residues, L62 and I79 (green) in gankyrin are highlighted.