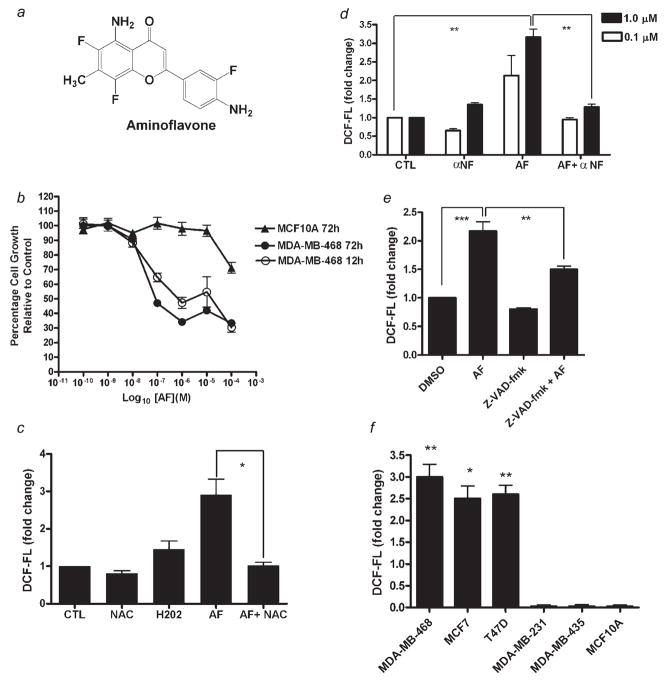
Figure 1.
Aminoflavone inhibits growth and increases ROS levels in sensitive cancer cells. (a) Structure of Aminoflavone (5-amino-2-(4-amino-3-fluorophenyl)-6,8-difluoro-7-methylchromen-4-one; AF; NSC 686288). (b) Exponentially growing malignant MDA-MB-468 and immortalized MCF-10A nonmalignant cells were treated with varying concentrations of AF or vehicle control (0.1% DMSO) continuously for 12 or 72 hr before Alamar Blue™ dye reagent was added and absorbance or fluorescence was measured to determine the anticancer activity of AF as determined in Materials and Methods. Data represent the mean of at least 3 independent experiments performed in quadruplicate; bars, SEM. (c) Cells were treated with negative control (CTL, 0.1% DMSO), 20 mM NAC, positive control (H2O2, 500 μM), AF (1.0 μM) or AF combined with NAC for 3 hr prior to analysis of ROS levels. Data represent the mean of at least 2 independent experiments performed in triplicate; bars, SEM. *p < 0.05 when comparing the 2 treatment groups. (d and e) Cells were treated with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO), 100 μM α-NF, 100 μM Z-VAD-fmk, AF (at the indicated concentrations in D or 1.0 μM in E) or AF following α-NF (1 hr) or Z-VAD-fmk (2 hr) pretreatment. Accumulation of intracellular ROS was detected by flow cytometry as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent the mean of at least 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate; bars, SEM. ***p < 0.001 or **p < 0.01 when comparing the indicated treatment groups. (f) Sensitive and insensitive breast cell lines were treated with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO) or 1 μM AF for 6 hr followed by measurement of increases in intracellular ROS levels as described above. Data represent the mean of at least 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate; bars, SEM. *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 when comparing ROS levels in sensitive cells vs. resistant cells exposed to 1 μM AF.