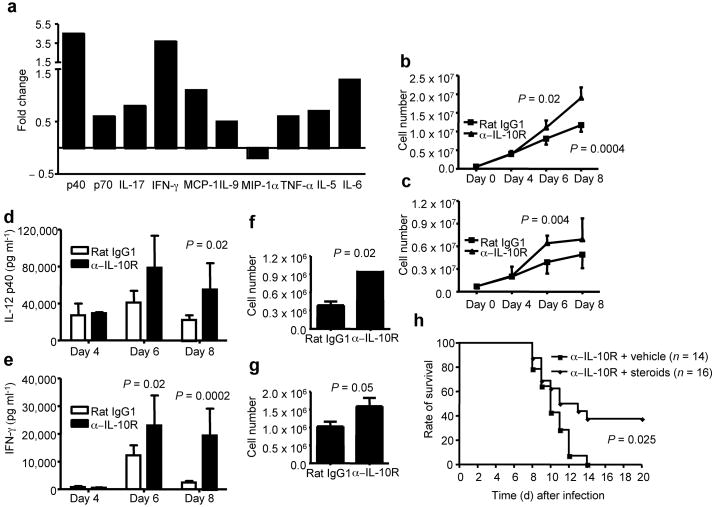
Figure 6. IL-10R blockade leads to lethal pulmonary inflammation during influenza infection.
(a) BALB/c mice were infected with influenza and treated with IL-10R-specific mAb (α-IL-10R) or Rat IgG1 control mAb (Rat IgG1). At day 8 p.i., cytokines in the BALF were determined by Multi-plex cytokine array analysis. Shown are the fold changes of cytokines in the BALF of IL-10R mAb treated mice vs. those of cytokines in the BALF of Rat IgG1 treated mice. (b, c) BALB/c mice were infected with influenza and treated with IL-10R-specific mAb (α-IL-10R) or Rat IgG1 control mAb (Rat IgG1). At day 4, 6 and 8 p.i., lung inflammatory monocytic cells (b) and neutrophils (c) were determined by flow cytometry. P value was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student t test. (d, e) BALB/c mice were infected with influenza and treated with IL-10R-specific mAb (α-IL-10R) or Rat IgG1 control mAb (Rat IgG1). At day 4, 6 and 8 p.i., IL-12 p40 (d) and IFN-γ (e) levels in the BALF were determined by ELISA. P value was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student t test. (f, g) BALB/c mice were infected with influenza and treated with IL-10R-specific mAb (α-IL-10R) or Rat IgG1 control mAb (Rat IgG1). At day 8 p.i., lung cells were restimulated with flu infected BMDC and the numbers of IFN-γ+ CD4+ (f) and IFN-γ+ CD8+ (g) T cells were quantified by ICS. P value was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student t test. (h) BALB/c mice were infected with influenza and treated with IL-10R-specific mAb plus vehicle control (α-IL-10R + vechicle) or IL-10R-specific mAb plus corticosterone (α-IL-10R + steroids). The survival of the mice was monitored daily. P value was determined by the Log-Rank survival test.