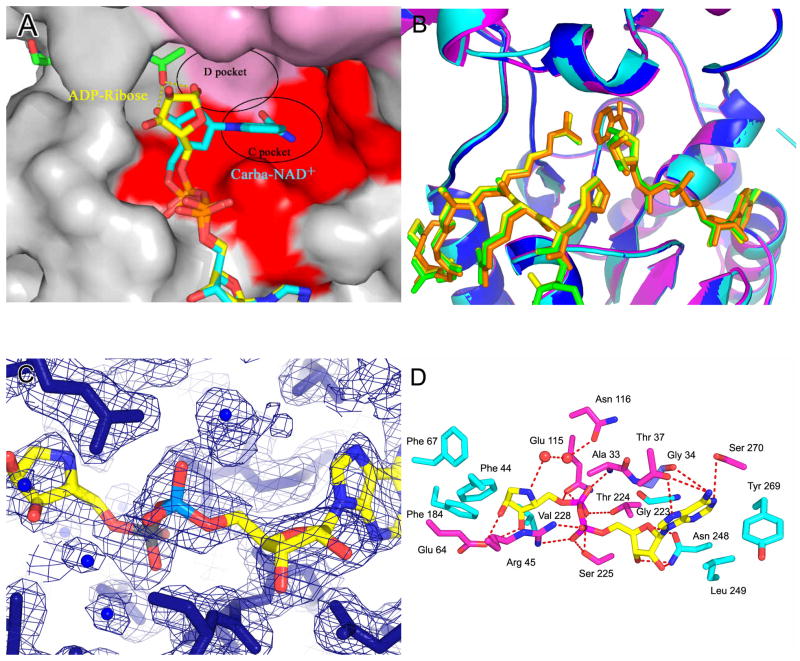
Figure 1. Structures of the free yHst2/ADP-HPD/histone H4 complex.
(A) Ternary yHst2 (gray) complex, highlighting strictly conserved (pink) and conserved (red) residues, the binding sites of acetyl-lysine (green), carba-NAD+ (cyan) and ADP-ribose (yellow) and the conserved C and D pockets. Hydrogen bonds between the acetyl-lysine and carba-NAD+ are shown as yellow dotted lines. Residues 43–48 of the flexible loop and residue 64 were omitted for clarity.
(B) Superimposition of the yHst2/ADP-ribose/H4 complex (magenta) with the yHst2/ADP-HPD/H4 complex (cyan) and the yHst2/ADP-HPD/H4 complex bound to nicotinamide (blue). The intermediate analogue, acetylated histone H4 ligands, and nicotinamide are shown in green for the ADP-ribose complex, yellow for the free ADP-HPD complex, and orange for the nicotinamide bound ADP-HDP complex.
(C) Simulated annealing omit density contoured at 1.0 sigma showing density for the protein (blue) and ADP-HPD (atoms individually colored). Water molecules are shown as blue spheres.
(D) yHst2 bound to ADP-HPD (atoms individually colored) and highlighting residues that make hydrogen bonds (red dashed lines) or van der Waals contacts with ADP-HPD. Hydrogen bonding residues are colored pink, residues that make van der Waals interactions are colored cyan, and residues that make both interactions are colored purple.