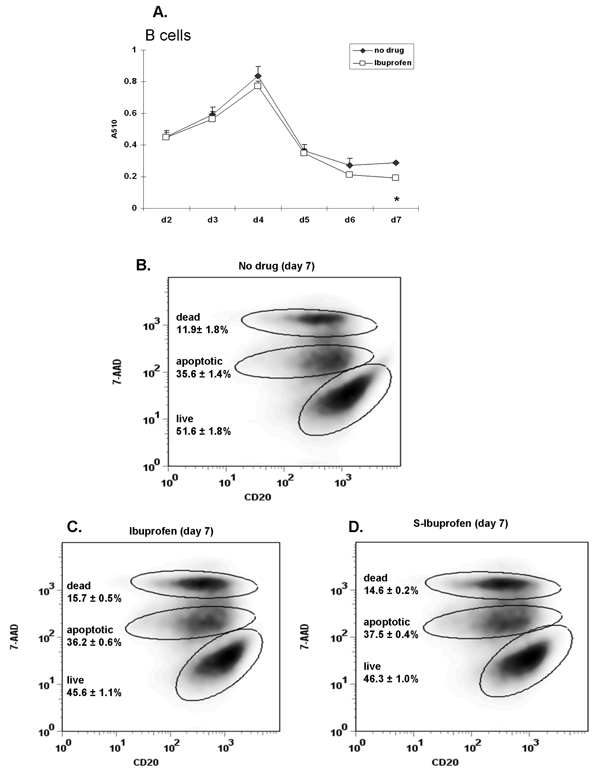
Figure 8. Ibuprofen only modestly inhibits purified B cell viability.
Purified human peripheral blood B cells isolated from 2 different donors were stimulated with anti-IgM (2 µg/ml) plus CpG 2395 (1 µg/ml) and were exposed to ibuprofen (50 µM; added daily) for 7 days. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay (donor 1) and by 7-AAD staining (donor 2). (A) The absorbance (A510 nm) values of ibuprofen-treated samples were similar to control (no drug) samples throughout day 2 to day 7. (B) Cells were surface stained for CD20 followed by 7-AAD staining and were analyzed by flow cytometry. A total of 15,000 events were acquired in each sample. Viable cells do not incorporate 7-AAD compared to apoptotic (7-AAD intermediate) and dead cells (7-AAD bright). The percentage of live, apoptotic and dead cells is similar in ibuprofen- (panel C) and S-Ibuprofen (panel D) treated samples. Cell percentages represent the mean values (n=3) with the corresponding SD. *, p< 0.05 (see panel A) was calculated using one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test.