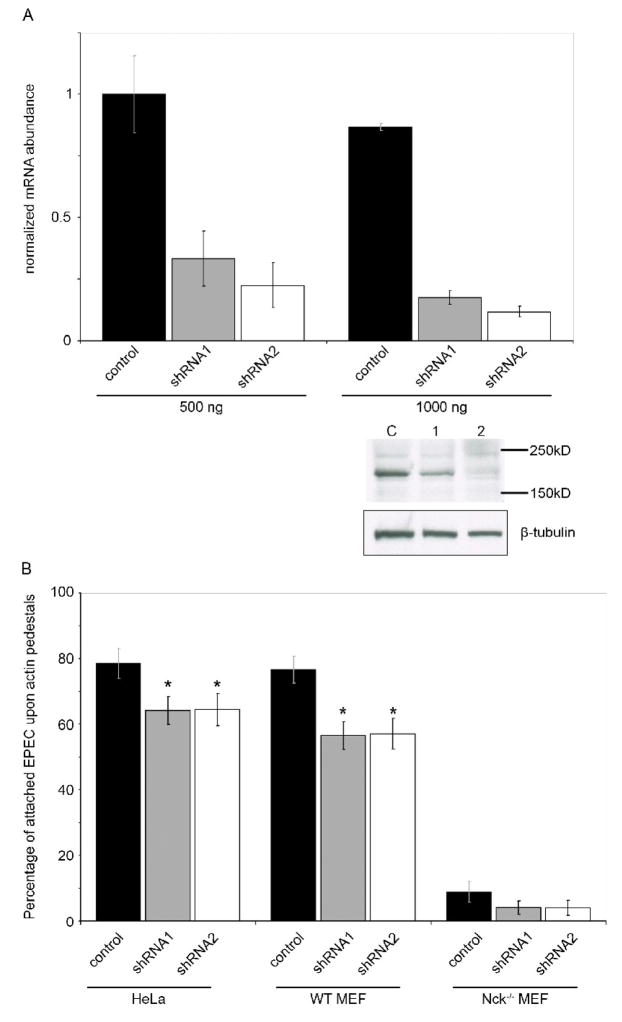
Figure 4. Shank3 deficient cells are less able to support efficient EPEC pedestal formation.
(A) HeLa cells were transfected with two levels of control shRNA vector (black bars) or one of two shank3-targeting shRNA vectors (grey and white bars). After 48 hours knockdown was assessed using real-time quantitative RT-PCR with Shank3 specific primers and normalized to GAPDH. Shown are means of two experiments, each using two independent cDNA samples, with standard deviations. A representative western blot following high-level (1000 ng) transfection of shRNA vectors is shown. Levels of endogenous Shank3 (as determined with anti-Shank3 antibody) are reduced in cells receiving Shank3-directed shRNAs 1 and 2, compared to control-transfected cells. Anti-tubulin is shown as a protein-level control.
(B) HeLa cells, WT MEFs or Nck−/− MEFs were transfected with shRNA constructs for 48 hours, then infected with EPEC for 6 hours as described. Pedestal formation was assessed by F-actin staining and is expressed as a percentage of total adherent bacteria. Means of data pooled from three independent experiments are shown, at least 40 cells per condition were counted in each experiment. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals, * signifies statistical significance p<0.05. Significance was measured using a two-sample T-test, comparing to the relevant shRNA control samples. Data is representative of three independent experiments.