Abstract
A robust peptide quantification method was developed where overlapping peptide isotopic distributions were fit with predicted peptide isotopic envelope mixture models (IEMM). Application to two difficult quantitative problems was demonstrated. The first was the quantification of deamidation, where masses of isotopic peaks differ by a single Da, and the second, 18O labeling, where the isotopic peaks are shifted 2 and 4 Da. In both cases, peptide quantification cannot be performed by simple integration of extracted ion chromatograms, because the isotopic envelopes of mass shifted peptides are normally not resolved. To test the methodology for quantification of deamidation, several synthetic peptides and their corresponding deamidated forms were mixed at various ratios (1:0, 1:2, 2:1, 4:1, 10:1 and 20:1) and analyzed using the IEMM method, resulting in a high correlation (R2=0.96) between measured and known percentages of deamidation. The IEMM method was then incorporated into a workflow for deamidation quantification in a large-scale proteomics experiment. A series of normal (3-day, 2-year, 35-year, and 70-year) and cataractous (93-year) human lenses were analyzed using two-dimensional liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and deamidation quantities of several γS-crystallin peptides ([N14-Q16], N53, [Q63–Q70], and N143) were determined. Two peptides (N53 and [Q63–Q70]) had more extensive deamidation in the water-insoluble portions of normal lens samples, and deamidation at N143 was more extensive in the 93-year water-insoluble cataractous sample. The utility of the technique for analysis of 18O-labeled peptides was examined using mixtures of labeled BSA peptides in known 16O to 18O ratios (10:1, 4:1, 1:1, 1:4, and 1:10). The methodology allowed accurate measurements of ratios of 16O/18O peptides over the wide range of relative abundances.
Keywords: Proteomics, mass spectrometry, bioinformatics, human lens, deamidation, Q-TOF, post-translational modification, crystallin, reverse-phase chromatography, isotopic envelope modeling, quantification, insolubility, cataracts, 18O labeling, software
INTRODUCTION
Software applications for quantitative proteomic studies have been recently reviewed1, and quantitative techniques were broadly categorized into spectral counting, isotopic labeling, or label-free quantification. Most quantitative methods attempt to determine relative protein abundance differences based on measurements of tryptic peptides from those proteins. The biological question, sample material, study design, and available instrumentation usually determine the most appropriate quantitative mass spectrometry method. It is not surprising that there is a great diversity of quantitative techniques in routine use.
Most quantitative software programs calculate relative ratios of isotopically labeled peptides pairs by summing ion intensities over an m/z range to produce an ion chromatogram that is then integrated. This procedure works well if the mass shifts of the peptide pairs are large enough to completely resolve the isotopic peaks, or co-elution of nearly isobaric peptides doesn’t occur. However, when the shift is below 6 Da, or nearly isobaric peptides co-elute, it becomes necessary to examine the isotopic peaks of the peptides in order to separate incompletely resolved isotopic peaks from one another and obtain accurate relative ion currents.
Our previous studies of human lens tissue identified deamidation as the major age-related PTM2, 3. Spectral counting was used to characterize differences in overall deamidation between young and old lens, but counts of individual peptides containing deamidation sites were often not large enough for reliable quantification. Measurements of the extent of deamidation at many sites are needed to understand how deamidation contributes to loss of protein solubility in lens tissue. Deamidation is important in aging studies,4 aggregation disease studies,5, 6 and in protein pharmaceutical studies,7 where it is often responsible for loss of protein function. Deamidation is difficult to detect because it introduces a small (+0.984 Da) mass shift, and non-deamidated and deamidated peptides behave similarly during reverse phase chromatography. Shallow gradients can be used to resolve deamidated peptides from their amidated forms2, 3, but overlapping chromatogram signals are more typical with nanospray chromatography and steeper gradients. Manual fitting of isotopic distributions has been previously used to calculate the extent of deamidation in peptides from lens crystallins8, 9, but this method is too cumbersome when analyzing complex digests.
Many additional PTMs besides deamidation exist in lens, and 18O labeling could be used to measure differences in the relative abundances of modified peptides between lens samples. Peptides with overlapping isotopic distributions frequently occur during 18O labeling as a result of incomplete label incorporation or back exchange10, 11. As mentioned above, most isotopic labeling software programs are not designed to deconvolute overlapping isotopic distributions which makes automated analysis of 18O labeled data particularly challenging. Thus a single tool to quantify differences in the extent of deamidation as well as quantify the relative abundance of 16O and 18O labeled peptides would be useful.
In this report, we have developed a Java application that was used with high-resolution Q-TOF data to determine the relative extent of deamidation at specific sites in human lens samples. The Mass Ion Current Integration Toolkit (MICIT) uses theoretically predicted isotopic distributions and an idealized instrument response function to calculate total ion current from overlapping mass shifted peptide forms using an isotopic envelope mixture model (IEMM). This enables deconvolution of overlapping m/z signals of amidated and deamidated forms of peptides, as well as overlapping m/z signals of 16O/18O labeled peptides. Since the signal processing occurs in m/z space, the methodology is tolerant of complex chromatogram peak shapes that would be difficult to integrate, as well as interference from co-eluting peptides with similar m/z values. The software supports multi-dimensional separations used for analysis of complex mixtures of peptides, and has an informative graphical user interface (GUI) to efficiently combine validation and quantification into one workflow.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample Processing
Synthetic peptides corresponding to human βB1 crystallin (SwissProt P05813) residues 150–159 (ISLFEGANFK) and residues 202–213 (GYQYLLEPGDFR) and their deamidated forms (ISLFEGADFK and GYEYLLEPGDFR, respectively) were obtained from Sigma Genosys (The Woodlands, Texas) and diluted to 10 pmol/μl in 5% formic acid. Peptides were analyzed by RP LC-MS, either alone or by simultaneously injecting mixtures of unmodified and deamidated forms of the same peptide at various ratios (1:0, 1:2, 2:1, 4:1, 10:1 and 20:1).
Lenses from 3-day, 2-year, 35-year, 70-year old human donors with healthy vision and a 93-year old human donor with type-III nuclear cataracts (Pirie scale) were obtained from the Lions Eye Bank of Oregon with Oregon Health & Science University IRB approval. To assess the accuracy of deamidation quantification, we analyzed the 3-day old lens (where little or no deamidation is expected). Lens proteins were separated into water-soluble and water-insoluble fractions by centrifugation, assayed for protein content, digested using trypsin, and separated by SCX chromatography as previously described3. The amount of water-insoluble portion of the 3-day old lens sample was negligible and could not be analyzed.
Immobilized Trypsin Preparation
Ten mg of trypsin (Worthington, cat# LS003740) was dissolved in 1 ml of 0.5 M Sodium Sulfate, 0.1 M Sodium Carbonate, 0.05 M benzamidine, pH 10.0 and added to a centrifuge tube containing 50 mg of Ultralink Biosupport beads (Pierce, Rockford, IL). The sample was incubated while rotating (end to end) at 37 °C for 1 hour, centrifuged at 2,000 × g at 25 °C for 2 minutes to pellet the beads, and the supernatant removed. To block non-reacted sites, the beads were washed once with 1 ml 1M ethanolamine pH 9.0, the wash discarded, and an additional 1ml 1M ethanolamine pH 9 added. After vortexing to mix, the sample was gently agitated for 2 hours at 37°C. Beads were then washed twice with 1.5 ml of 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, twice with 1.5 ml of 1.0 M NaCl, and finally twice with 1.5 ml of 50 mM Tris pH 7.5. The final pelleted beads were then stored suspended in 1 ml of 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 0.02% sodium azide.
Preparation of 16O/18O Mixtures
One mg BSA (A1900, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was dissolved in 100 μl of 8M urea, 0.8 M Tris, 0.2 M methylamine, and 8 mM CaCl2 (pH 8.5). After reduction and alkylation with DTT and iodoacetamide, respectively, the urea concentration was diluted to 2M by addition of water and 40 μl immobilized trypsin. Immobilized trypsin (described above) was prepared by washing 50 μl of the suspended beads 3 × in 250 μl of water, followed by resuspension in 50 μl of water. Digestion occurred overnight at 37°C while shaking (MT-360 microtube mixer, setting of 7, TomyTech USA, Inc. Fremont, CA). After trypsin removal by centrifugation and solid phase extraction of the peptides using Sep-Pak light cartridges (part #WAT023501, Waters, Milford, MA), 100 μg portions of the digests were taken to dryness. Two dried 100 μg portions of the BSA digest were then incubated in either H216O or H218O in the presence of additional immobilized trypsin to catalyze exchange of the two C-terminal oxygen atoms. Five μl of 250 mM histidine, 5 mM CaCl2 (pH 6.0) and 8 μl of suspended immobilized trypsin (prepared as above) was added to each sample, followed by drying using vacuum centrifugation. Forty-five μl of either H216O or H218O (95% enriched, Isotec, Miamisburg, OH) was then added to each tube, followed by 5 μl of acetonitrile. The samples were again shaken overnight as above, and immobilized trypsin removed by filtration (Ultrafree-MC spin filters, Millipore, Bedford, MA). Peptides were then diluted to 1 pmol/μl in 1% acetic acid, mixed at ratios of 10:1, 4:1, 1:1, 1:4, and 1:10 (16O:18O), and 10 pmoles analyzed by mass spectrometry within 12–24 hours to minimize back exchange.
LC-MS/MS Analysis
Synthetic peptides, peptide mixtures, 10% portions of SCX fractions of lens digests, and 18O-labeled BSA mixtures were analyzed by LC-MS using a Waters capillary LC system and a Q-TOF2 mass spectrometer (Waters, Milford, MA). Samples were applied at 15 μl/min to a Nanoease C18 trap cartridge (Waters, Milford, MA), and then switched onto a 0.15 × 150 mm Nanoease Symmetry C18 column (Waters, Milford, MA) using a mobile phase containing 0.1% formic acid. The gradient used 9.4–37.5% acetonitrile over 95 min at a 0.4 μl/min flow rate. Survey and MS/MS scans were collected in profile mode. Some of the BSA ratio analyses were acquired without MS/MS scans to improve MS data quality. Data dependent MS/MS collection used charge state dependent dynamic exclusion feature (exclusion mass window width 3.0 Da, repeat count of 1, exclusion list size 80 ions, and exclusion duration of 10 sec) to obtain MS/MS spectra of the five most abundant parent ions following each 1-second survey scan. DTA files were generated using ProteinLynx software (Version 2.1, Waters, Milford, MA) with an m/z range of 50 to 2000 Daltons. Profile peaks in MS/MS scans were smoothed with a Savitzky-Golay filter (2 iterations with 3 channels) and centroided to generate DTA files. A total of 133,374 tandem mass spectra were acquired from all LC-MS/MS experiments of lens digests. Peak areas of synthetic peptides were determined from MS scans by generating extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) using MassLynx software (Waters).
Peptide Identification
Lens peptides were identified by searching the MS/MS spectra against a human lens database described previously2 using SEQUEST12. BSA samples were searched against a bovine species subset of SwissProt (UniProt Release 10.3; April 17, 2007 download; 3420 entries). Searches were configured to use monoisotopic masses, the parent ion mass tolerance was 0.5 Da, a static mass of 57.02 was specified for alkylated cysteine residues, and “no enzyme” cleavage was specified. The following variable modifications were also specified while searching for human lens peptides: deamidation (+0.984 Da on N or Q); oxidation (+15.995 on M or W); and acetylation (+42.011 Da) on the N-terminus of peptides. A variable modification of +4.0 Da on K and R residues was specified while searching for BSA peptides. A list of peptides, proteins, and potential post-translational modifications was generated using DTASelect13 with XCorr thresholds of 1.8, 2.5, 3.5, and 3.5 for +1, +2, +3, and +4 parent ions, respectively; a minimum DeltaCN of 0.0 (instead of default 0.08); and full or half-tryptic peptides only.
Deamidation Quantification with IEMM
A quantification method was developed that modeled the parent ion isotopic envelope as a mixture of different peptide forms using a Gaussian instrument response function. For the lens samples, the peptide forms corresponded to unmodified and deamidated peptide forms. Peptide forms having zero, one, or two 18O atoms were used for the 18O labeled BSA samples. In this model, the total calculated ion current intensity Y at m/z value x is given by:
| (1) |
where Ij are intensity factors proportional to the total ion current of peptide form j, p is the total number of peptide forms included in the model, fij are the predicted fractional relative intensities of the i isotopic peaks of peptide form j calculated using a method similar to Reference 14, are the positions of the ith isotopic peak of peptide form j, and σij are the widths of the ith isotopic peak of peptide form j, B(x) is the background intensity contribution from the mass spectrometer which is modeled as either a quadratic or cubic polynomial.
To compensate for small difference between measured and theoretical masses, the peak position parameter is allowed to vary during model optimization and is given by:
| (2) |
where Ck are polynomial m/z calibration correction coefficients, Mij are the charge-to-mass values of the ith isotopic peak of peptide form j, and xo is the beginning m/z value of the fitting interval. The charge-to-mass values of the ith isotopic peak of peptide form j are calculated according to Eqn. 3 from the molecular weights, MWij, and peptide charge z.
| (3) |
The peak width parameter σij is given by:
| (4) |
where Sk are polynomial coefficients to calculate σij at position Mij, and xo is defined as in Eqn. 2. The order of and σij functions are dependent on the choice of mass spectrometer. Higher-order terms in and σij are required for low-resolution ion trap instruments where distortions from space charging are more common, however, lower order polynomial functional forms could be used with Q-TOF instruments to reduce the number of degrees of freedom in the fitting process. The intensities of unmodified and deamidated peptides or 18O labeled peptide mixtures with 0, 1, or 2 18O atoms were varied until the best agreement between the total calculated ion current and the measured isotopic envelope was obtained.
Optimizing IEMM Parameters
The m/z peak shapes resemble high resolution x-ray or γ-ray spectra where similar theoretical modeling is often used15. Non-linear least squares minimization method is typically used to determine optimal model parameters from such bivariate data16. We have utilized the MnMiGrad routine of the function minimization toolkit Minuit (version 1.7.6, CERN, Geneva; http://seal.web.cern.ch/seal/documents/minuit/mnusersguide.pdf) to perform the minimizations. Model parameters were optimized in a two step process to ensure robust convergence. In the first round, all peak parameters were optimized assuming a constant instrument background response. In the second round, peak parameters were held constant and an appropriate higher order background was determined. Since relative peak positions are based on theoretical mass calculations and time-of-flight instruments can have temperature-dependent calibration changes during the course of an LC run, we allowed peak positions to vary (Eqn. 2) during the minimization process. It is important for convergence to have the theoretical and measured peak positions coincide because small discrepancies can cause large squared residuals. This is not mass recalibration in the traditional sense and correction factors for the QTOF were often very small (less than 0.1 Da).
Quantification Workflow
A semi-automated workflow for large-scale deamidation quantification in complex samples was developed. The quantitative software accepts native Q-TOF2 (Waters, Milford, MA) instrument files and OpenSea17 formatted XML files for MS/MS results. Scripts were written to convert SEQUEST output to OpenSea XML files. Peptide identifications containing deamidation sites and their corresponding chromatography coordinates (SCX fractions and RP retention times) are extracted from the MS/MS results. Peptide identifications are grouped by parent protein, primary (unmodified) peptide sequence, observed SCX fractions, and charge states.
Protein and peptide information is displayed in an expandable tree table. Selection of a specific peptide produces a combined extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) based on the theoretical unmodified peptide monoisotopic mass and any additional deamidated peptide forms. Retention times (RT) of MS/MS identifications are indicated on the chromatogram tracings. After selection of an RT range encompassing all peptide forms of interest, profile-mode MS survey scans are averaged within the RT range in a five Da window (in m/z space) centered on the unmodified peptide monoisotopic m/z value for the selected charge state. The measured mass ion currents in the narrow m/z range are shown along with the initial IEMM model and associated parameters. The initial model parameters can be changed, if necessary, before the least-squares function minimization is initiated. After minimization, final IEMM calculated intensity is overlaid on the measured m/z ion intensity distribution and final parameters are displayed. Results of the IEMM fitting are saved in an XML file format for subsequent report generation. Supplemental File 1 contains screen snapshots of the application window during analysis of a deamidated peptide. Pseudo-code detailing program operation is given in Supplemental File 2.
The MICIT was written in a combination of Java and C++ programming languages for Windows XP. The MassLynx DAC library (Waters, Milford, MA) has to be installed prior to running MICIT. Interactive analysis time is usually less than a minute per peptide and total analysis time will depend on sample complexity. The software is available for non-commercial use from the authors upon written request via material transfer agreement with Oregon Health & Science University (Portland, OR). No support for instrumentation other than the Waters QTOF platform has been attempted. Deamidation and 18O labeling are the only two fitting options at this time.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Testing Deamidation Quantification Using Synthetic Peptide Mixtures
We have previously shown that unmodified and deamidated peptides can be resolved by shallow RP gradients2 which would, in principle, allow XIC areas to be used for relative ion current measurement of each peptide form present. However, many factors make this approach problematic in practice. Isomerization following asparagine deamidation creates isomeric products that have different elution times which fractionates deamidated peptide ion currents and can cause overlap with ion currents from the unmodified peptides2. Poor chromatography peak shapes and long RT tailing can also cause mixing of ion currents from unmodified and deamidated peptides making reliable detection of low deamidation levels challenging. Interfering peptides in complex mixtures are also a common source of error in quantitative studies.
Data from LC-MS experiments are typically ion intensities as a function of two coordinates: RP retention times and m/z values. Ion currents of interest are most commonly measured by specifying a narrow range in m/z space and projecting the ion currents onto the RT coordinate (XIC). Alternatively, it is mathematically equivalent to set a window in RT space and project ion currents onto the m/z coordinate. Projections onto either coordinate should yield identical ion currents.
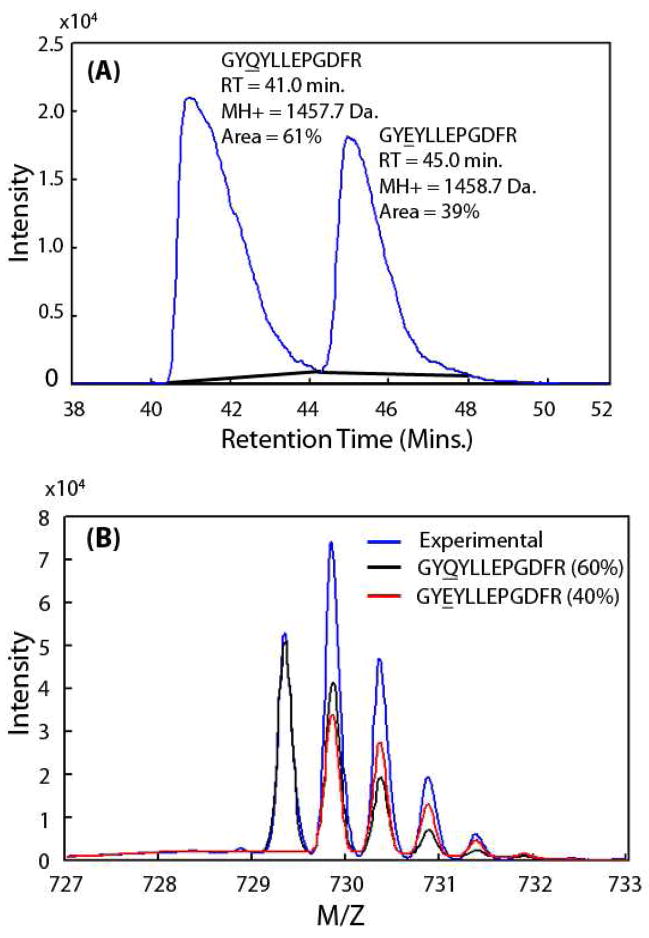
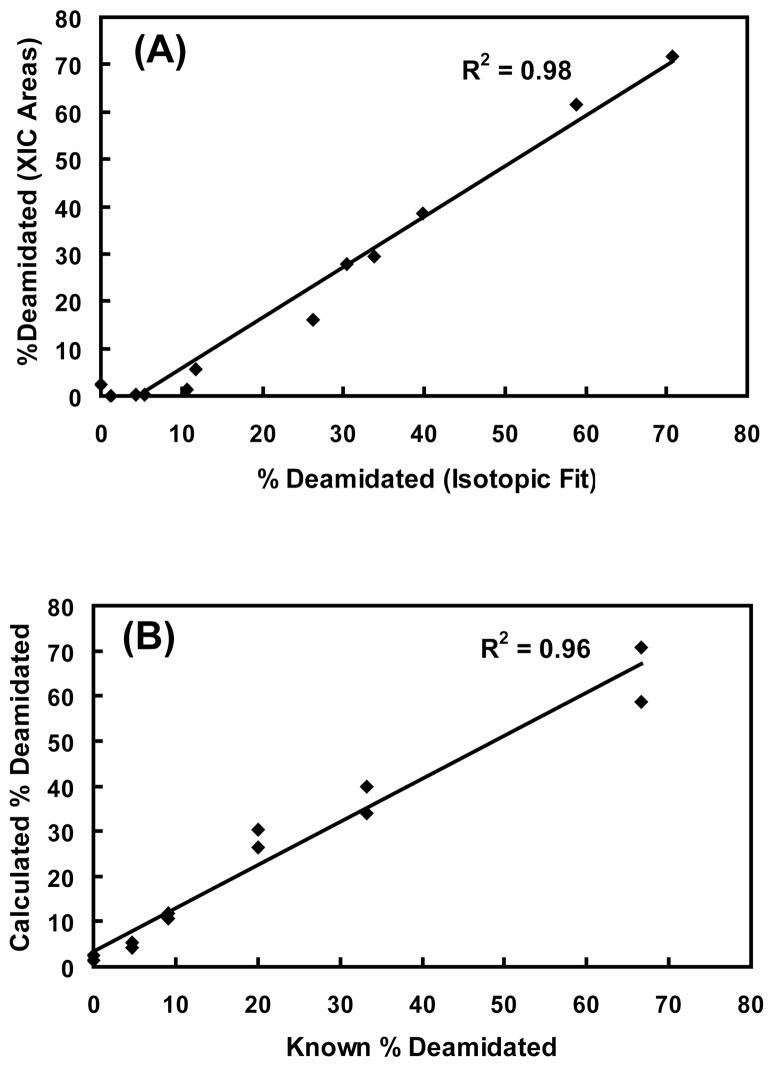
To compare these two equivalent ion current integration methods over a wide range of simulated deamidation levels, synthetic peptide pairs where amides have been replaced by acids were used to simulate in vivo deamidation without complications from isomerization or interfering peptides. In Figure 1A, the XICs and peak areas of peptides GYQYLLEPGDFR and GYEYLLEPGDFR are shown. The relative ion currents obtained by IEMM analysis are shown in Figure 1B, and are in excellent agreement with those from XIC net peak areas. The high correlation between XIC ion currents and IEMM ion currents is shown in Figure 2A from two different synthetic peptide pairs mixed in six known amounts. The accuracy of the IEMM method is shown in Figure 2B where IEMM-calculated deamidation levels are plotted against the known mixture values, and the IEMM method accurately determined both high and low levels of deamidation. Traditional XIC integration techniques may become unreliable in measuring deamidation present in low stoichiometric levels due to the difficulties in detecting weak peptide ion chromatogram peaks (see lower quadrant of scatter plot in Fig. 2A).
Figure 1. Comparison of IEMM and XIC integration methods.
Combined ion trace of synthetic peptide GYQYLLEPGDFR (βB1 crystallin, 202–213) and its deamidated form (GYEYLLEPGDFR) is shown in panel (A). The solid black lines are the baselines used to determine net peak areas. The combined m/z spectrum shown in panel (B) in blue was obtained by averaging MS scans from 40.4 to 48.0 minutes. The resulting IEMM fits for the unmodified peptide (black) and the deamidated peptide (red) isotopic envelopes are also plotted. The XIC integration and IEMM results, shown in (A) and (B) as percentages, agreed very well.
Figure 2. Equivalence between XIC and IEMM methods and accuracy of IEMM method.
Known mixtures of amide to acid synthetic peptides were analyzed by LC-MS. Experimental ratios of deamidated ion current (peptide with acid residue) to total ion current (sum of amide and acid forms) measured using IEMM and extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) methods are expressed as percentages and compared in panel (A). A high correlation was observed between the two methods. Calculated IEMM method deamidation ratios are plotted against the known ratios in panel (B) and excellent correlation was observed between the known and calculated ratios at both high and low deamidation ratios.
Complex Mixtures
Co-eluting peptides frequently complicate XICs in complex samples and make accurate quantification difficult. A range of m/z values encompassing the +2 ions of the various peptide forms (unmodified, singly deamidated, and doubly deamidated) of ITIYDQENFQFK (αA-crystallin, 33–44) from a representative SCX fraction of 93-year old lens insoluble protein digest was used to create the combined ion chromatogram (CIC) shown in Figure 3A. The chromatogram is far more complex than those from simple mixtures (Fig. 1A) and would require some type of deconvolution into individual chromatogram peaks to obtain accurate ion currents of the constituent peptides. The peaks in the chromatogram are not baseline resolved, making background estimates error-prone and the complex peak shapes are more difficult to model. The MS scans during 34.0 to 42.0 min. were averaged to obtain the total experimental ion currents from the peptide forms and are shown in Figure 3B. The experimental total MS intensity was modeled using a mixture of predicted isotopic envelopes of unmodified, singly deamidated, doubly deamidated peptide forms, and a cubic polynomial background. Individual components are shown in Figure 3B and total calculated and measured MS ion currents are shown in Figure 3C. The unmodified, singly, and doubly deamidated peptide ion currents relative to the total ion current could be accurately measured and were 31%, 39% and 30%, respectively. The theoretically predicted isotopic envelope distributions and high-resolution data make signal deconvolution in m/z space much simpler than deconvolution of complex chromatogram peaks.
Figure 3. Advantages of IEMM over XIC integration in complex samples.
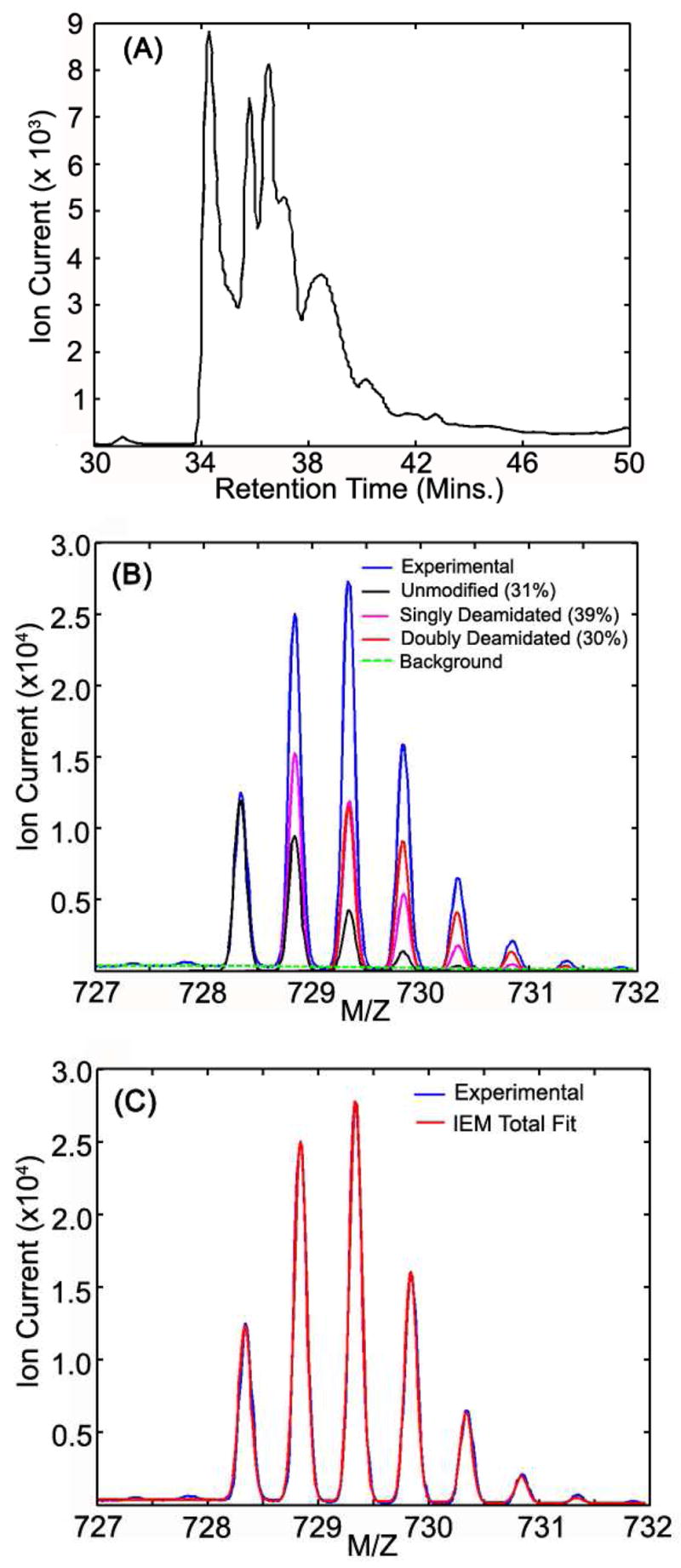
Combined ion traces for peptide ITIYDQENFQGK (αA-crystallin 33–44) and its deamidated forms from a 93-year old insoluble SCX fraction are shown in panel (A). MS scans from 34 to 42 min were averaged and IEMM fits with unmodified, singly deamidated, and doubly deamidated peptide forms (and their corresponding relative areas) are shown in panel (B). Composite IEMM fit is overlaid on experimental averaged mass spectrum in panel (C) to illustrate the quality of the IEMM modeling.
Mass Ion Current Integration Tool (MICIT)
The mass ion current integration tool (MICIT) was developed as a GUI that performs deamidation quantification using the IEMM method. The interface allows the user to interactively drive the quantification process using search engine results. The software consolidates disparate information sources such as protein identifications, peptide identifications, their corresponding MS scans, and multi-dimensional chromatographic coordinates (SCX fractions and RP retention times) in a single user interface. Contemporary multi-dimensional liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry experiments often contain large numbers of protein and peptide identifications present in multiple fractions and quantification in such complex datasets would become cumbersome without a tool like MICIT.
γS-Crystallin Peptide Deamidation Rates
Peptides containing deamidation sites from a series of human lenses were identified using SEQUEST, and the results loaded into MICIT for processing. In a preliminary analysis, averaged mass chromatograms were generated for all SCX fractions where peptides from γS, one of the abundant lens crystallin proteins, were identified, and different charge states (distinct m/z values) were processed independently. Peptide retention time integration boundaries for each SCX fraction were determined using a 2.5% baseline threshold in the corresponding combined ion chromatograms. The ion currents of different peptide forms present in averaged spectra were calculated using the IEMM method. Peptide ion currents from all SCX fractions were grouped by charge state and summed according to peptide form (unmodified, single deamidated, etc.). Relative percent deamidation (deamidated ion current as a percentage of total peptide ion current) was calculated for each observed charge state and the overall percent deamidation was computed by averaging over all charge states.
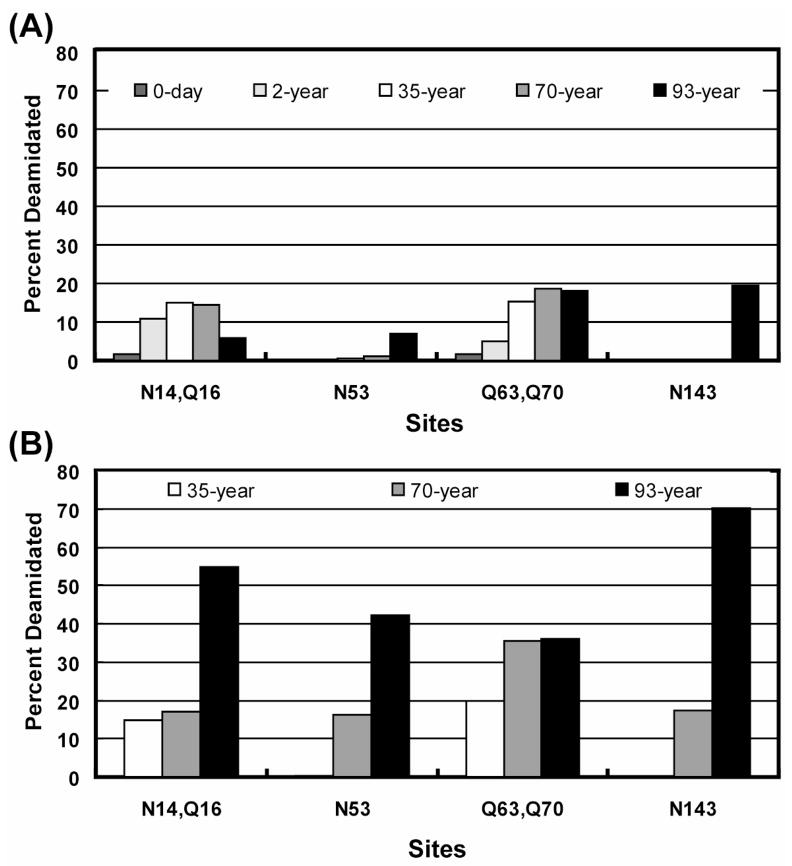
Relative percent deamidation of sites [N14-Q16] (ITFYEDKNFQGR), N53 (VEGGTWAVYERPNFAGY), [Q63–Q70] (MYILPQGEYPEYQR), and N143 (IFYELPNYR) in γS-crystallin were computed using the above protocol for water-soluble portions of 3-day, 2-year, 35-year, 70-year old normal human lenses, and a 93-year old cataractous human lens, as well as for the water-insoluble portions of 35-year, 70-year normal lenses, and 93-year old cataractous human lenses. Both single and double deamidation abundances were computed for peptides with two potential deamidation sites. The computed single deamidation abundances of these γS-crystallin sites in water-soluble and water-insoluble protein are shown in Figures 4A and 4B, respectively. The percentage double deamidation rates of peptides containing [N14-Q16] and [Q63–Q70] were very low for all samples except the water-insoluble fraction of the 93-year old lens (data not shown). Water-insoluble samples from 3-day and 2-year-old donors were not analyzed because this fraction was negligible in young lenses.
Figure 4. γS-crystallin peptide in vivo single deamidation abundances.
Single deamidation relative abundances (expressed as percentages) of peptides from lens γS- crystallin are calculated for (A) water-soluble and (B) water-insoluble fractions of an aged series of normal and cataractous human lens samples. Computed abundances in both fractions are plotted on the same scale. [Q63, Q70], N53, and N143 sites showed a pronounced deamidation increase in the water-insoluble fractions of human lens compared to corresponding water-soluble fractions. The water-insoluble portions of aged cataractous lens (93-year) sample showed an overall increase in deamidation at most of the sites compared to normal lens samples.
Previous studies have shown that structural changes in γS are correlated with its insolubility9, 18. The structure of γS consists of two N-terminal domains and two C-terminal domains connected with a peptide linker. Three N-terminal domain peptides ([N14-Q16], [Q63–Q70], Q53) and one C-terminal domain peptide (N143) from γS showed an increase in deamidation in the water-insoluble portions of lens samples compared to the corresponding water-soluble portions (Fig. 4.). Deamidation in the water-insoluble portions of an aged cataractous lens was also increased at three of the four sites compared to normal lens (Fig. 4B). These observations support the hypotheses that overall accumulation of deamidation contributes to loss of protein solubility during aging and that deamidation may be increased in cataractous lenses.
The N143 amide of γS (situated in first C-terminal domain) is localized in a highly ordered, folded β-hairpin loop, which plays a key role in maintaining a tertiary βγ fold19. Deamidation at this site has been postulated to destabilize this γS domain, leading to loss of protein solubility and changes in structure18, and earlier studies have detected deamidation of N143 in cataractous human lens samples9. We detected N143 deamidation rates only in the water insoluble portions of aged normal (70-year) and cataractous (93-year) human lens samples, but could not detect appreciable deamidation at this site in the other lens samples analyzed in this study. The extent of N143 deamidation observed in water insoluble and water soluble portions of cataractous (93-year) human lens sample agreed well with previous observations8, 9. Additional cataractous lenses need to be analyzed to see if γS N143 deamidation is indeed associated with catractogenesis.
Application to Proteolytic 18O labeling
Stable isotope labeling is an important technique in quantitative proteomics despite the fact that most labeling techniques have limitations. For example, chemically selective reagents (ICAT) do not label all peptides of interest, metabolic labeling (SILAC) cannot be used on tissue samples, and iTRAQ is moderately expensive and requires instrumentation that can detect small m/z reporter ions. Proteolytic 18O labeling20, on the other hand, is relatively inexpensive, labels nearly every peptide present in the sample and trypsin is already used extensively in most proteomic studies. However, 18O labeling is not without its list of flaws: catalyzed back-exchange can occur if there is any residual trypsin activity present and immobilized trypsins are usually required21. Digestion in complex mixtures may not be complete for all proteins and 18O incorporation may not be complete11. The labeled peptides will be a mixture of fully labeled (+4 Da) and partially labeled (+2 Da) forms which overlap in m/z values with the unlabeled peptides. Thus 18O quantitative software must deconvolute peptides with mixed m/z signals in much the same way as MICIT does for deamidation studies.
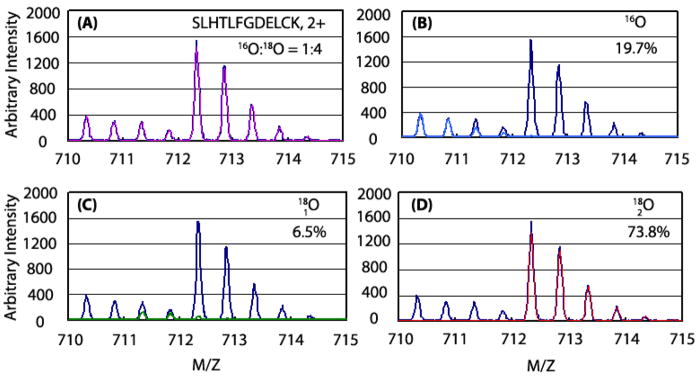
The IEMM method described in this report was adapted to deconvolute mixed isotopic signals arising from unlabeled (zero 18O atoms), partially-labeled (one 18O atom), and fully-labeled (two 18O atoms) peptide forms. Figure 5A compares the total experimental and modeled (IEMM) isotopic distributions of peptide 89SLHTLFGDELCK100 from a 1:4 mixture of 16O:18O labeled BSA digests. Individual isotopic signals of each peptide form (unlabeled, partially-labeled, and fully labeled) and percentage of ion currents accounted by each of the forms are shown in Figures 5B, 5C, and 5D, respectively. The experimentally determined 18O:16O ratio of 4.1 for the peptide was in excellent agreement with the expected ratio of 4.
Figure 5. Deconvolution of peptide signals in 16O:18O labeling experiments.
The composite IEMM fitted function (magenta) and experimental data (blue) of BSA peptide SLHTLFGDELCK from a 1:4 mixture of 16O and 18O labeled BSA standards is shown in panel (A). The contributing peptide forms and percentage of total ion current accounted by them are shown in panels (B) through (D) for peptides containing zero (sky blue), one (green), or two (red) 18O atoms, respectively.
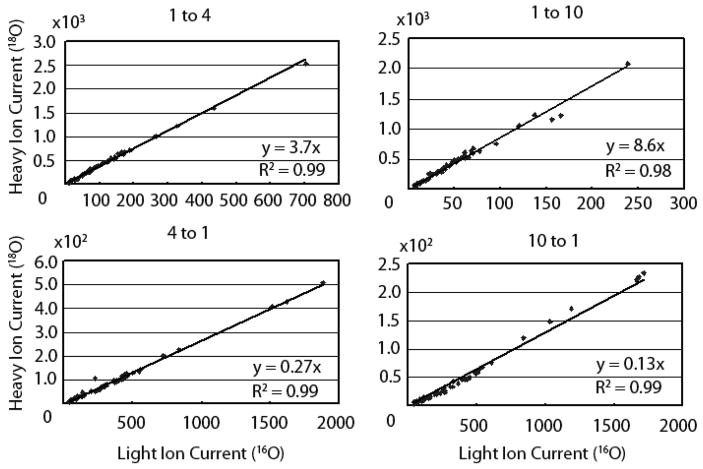
The accuracy of the IEMM method in determining correct ratios of isotopic labeled peptides was tested using a wide range (1:10, 1:4, 1:1, 4:1, and 10:1) of 16O:18O labeled BSA peptide mixtures. Mixtures were analyzed on a QTOF using either LC-MS or LC-MS/MS. Peptides present in LC-MS experiments were identified using the accurate mass and retention time tags22 that were derived from peptide identifications present in LC-MS/MS experiments. MICIT was used to determine ion currents of light (16O) and heavy (18O) forms of BSA peptides present in the known mixtures. Computed light and heavy peptide ion currents were corrected for back exchange and labeling efficiency using a previously described protocol10. Corrected light and heavy peptide ion currents from various known mixtures are compared in the ion current scatter plots shown in Figure 6. Data from the 1:1 mixture was similar in quality and is not shown. The slopes of the trend lines in the ion current scatter plots were used to compute the overall ratios of 18O to 16O in the BSA mixtures. Accurate heavy-to-light ratios were measured for peptides in all charge states over a wide dynamic range of individual peptide ion current intensities. The consistency of the individual peptide ratios in each mixture shown in Figure 6 was particularly striking.
Figure 6. Correlation of heavy and light peptide ion currents in known 16O:18O mixtures.
BSA standards were digested in presence of light (16O) and heavy (18O) water and a variety of known light:heavy peptide mixtures (1:4, 1:10, 4:1, and 10:1) were generated. Back-exchange corrected light and heavy peptide ion currents were computed from the individual peptide ion currents (determined using IEMM) for all identified BSA peptides in all detectible charge states. Peptide ion current correlation plots from different mixtures are shown in separate panels where the slope of the trend line represents the average ratio and the correlation coefficient indicates the consistency of the individual measurements.
Benefits and Limitations of the IEMM Method
The IEMM method and GUI allows visualization of the fitting and easy detection of interfering peptides or incorrect peptide sequence assignments. Interfering peptides can be common in complex mixtures and MS/MS identification software is far more tolerant of mixed peptides than is quantitative software. Stable isotope labeling essentially doubles m/z peak complexity and significantly increases the likelihood of interference. Outlier analysis may be ineffective if the interfering signal does not alter the expected ratio dramatically, or for proteins having small numbers of peptides. MICIT allows for a much more robust treatment of interference and individual measurements do not have to be discarded when the interference can be incorporated into the IEMM fitting. Incorrect sequence assignments can be identified provided the predicted relative isotopic intensities are sufficiently different from the actual distribution.
Our method relies on accurately modeling the measured data and works well on QTOF platforms with intermediate (typically 8,000 to 10,000) resolution. Similar resolution data can be obtained using slower, narrow-range scans on ion traps (Zoom scans) but space charging distortions are difficult to model and AGC settings are critical. Space charging distorts both peak positions and peak shapes (data not shown) and limits the applicability of our method. Very high resolution data10, 23 may not require such complicated modeling because the narrow peaks are usually free from interference and isotopic peaks can be grouped on the basis of their accurate masses. Net peak areas can be readily obtained and intensity corrections for contributions from isotopically-labeled partners computed. One advantage of our interactive method is that any discrepancies between calculated instrument response and measured data can be evaluated to provide another level of quality control. It is easy to test that relative peak positions and relative isotopic intensities agree with predicted values. Discrepancies could indicate instrument problems or incorrect peptide sequence identifications.
CONCLUSIONS
A new software package to reliably quantify deamidated peptides was developed. The program models the experimental total isotopic distribution with predicted peptide isotopic distribution to quantify deamidated peptides or other peptides with small mass differences. The method is robust and accurate when poor chromatography conditions or interfering peptides are present. The program operates within a semi-automated GUI (MICIT) that combines protein and peptide identifications with their corresponding MS data into a single user interface. A workflow that used MICIT for efficient quantification of deamidated peptides present in large-scale proteomics datasets was developed and tested. The software has obvious application to proteolytic 18O labeling, and accurate ratio measurements of BSA test mixtures spanning a wide dynamic range were demonstrated.
Supplementary Material
Story board illustrating the MICIT workflow for handling multi-dimensional datasets is shown in Supplemental File 1. Algorithm pseudo code is listed in Supplemental File 2. SEQUEST peptide identification results from all LC/MS/MS experiments are available as a Scaffold file (version 2.0) upon request. A free version of Scaffold viewer can be downloaded from www.proteomesoftware.com. The software is available for non-commercial use from the authors upon written request via material transfer agreement with Oregon Health & Science University (Portland, OR).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Hongyu Zhao for developing the immobilized trypsin protocol and D. Leif Rustvold for helpful discussions. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant U19ES11384 to Dr. Srinivasa R. Nagalla, and grants EY007755 and EY010572 to Dr. Larry L. David.
ABBREVIATIONS
- 2-DLC
Two Dimensional Liquid Chromatography
- GUI
Graphical User Interface
- IEMM
Isotopic Envelope Mixture Modeling
- MICIT
Mass Ion Current Integration Toolkit
- RP
Reverse Phase
- SCX
Strong Cation Exchange
- XIC
extracted Ion Chromatogram
References
- 1.Mueller LN, Brusniak MY, Mani DR, Aebersold R. An assessment of software solutions for the analysis of mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 2008;7(1):51–61. doi: 10.1021/pr700758r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dasari S, Wilmarth PA, Rustvold DL, Riviere MA, Nagalla SR, David LL. Reliable detection of deamidated peptides from lens crystallin proteins using changes in reversed-phase elution times and parent ion masses. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(9):3819–26. doi: 10.1021/pr070182x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wilmarth PA, Tanner S, Dasari S, Nagalla SR, Riviere MA, Bafna V, Pevzner PA, David LL. Age-related changes in human crystallins determined from comparative analysis of post-translational modifications in young and aged lens: does deamidation contribute to crystallin insolubility? J Proteome Res. 2006;5(10):2554–66. doi: 10.1021/pr050473a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McKerrow JH. Non-enzymatic, post-translational, amino acid modifications in ageing. A brief review. Mech Ageing Dev. 1979;10(6):371–7. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(79)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Watanabe A, Hong WK, Dohmae N, Takio K, Morishima-Kawashima M, Ihara Y. Molecular aging of tau: disulfide-independent aggregation and non-enzymatic degradation in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem. 2004;90(6):1302–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Watanabe A, Takio K, Ihara Y. Deamidation and isoaspartate formation in smeared tau in paired helical filaments. Unusual properties of the microtubule-binding domain of tau. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(11):7368–78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.11.7368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wakankar AA, Borchardt RT. Formulation considerations for proteins susceptible to asparagine deamidation and aspartate isomerization. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95(11):2321–36. doi: 10.1002/jps.20740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lapko VN, Purkiss AG, Smith DL, Smith JB. Deamidation in human gamma S-crystallin from cataractous lenses is influenced by surface exposure. Biochemistry. 2002;41(27):8638–48. doi: 10.1021/bi015924t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Takemoto L, Boyle D. Increased deamidation of asparagine during human senile cataractogenesis. Mol Vis. 2000;6:164–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mason CJ, Therneau TM, Eckel-Passow JE, Johnson KL, Oberg AL, Olson JE, Nair KS, Muddiman DC, Bergen HR., 3rd A method for automatically interpreting mass spectra of 18O-labeled isotopic clusters. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(2):305–18. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600148-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ramos-Fernandez A, Lopez-Ferrer D, Vazquez J. Improved method for differential expression proteomics using trypsin-catalyzed 18O labeling with a correction for labeling efficiency. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(7):1274–86. doi: 10.1074/mcp.T600029-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eng JK, McCormack AL, Yates JR., III An Approach to Correlate Tandem Mass Sectral Data of Peptides with Amino Acid Sequences in a Protein Database. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994;5:976–989. doi: 10.1016/1044-0305(94)80016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tabb DL, McDonald WH, Yates JR., 3rd DTASelect and Contrast: tools for assembling and comparing protein identifications from shotgun proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2002;1(1):21–6. doi: 10.1021/pr015504q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Senko MW, Beu SC, McLafferty FW. Determination of Monoisotopic Masses and Ion Populations for Large Biomolecules from Resolved Isotopic Distributions. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1995;6:229–233. doi: 10.1016/1044-0305(95)00017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aarnio PA, Nikkinen MT, Routti JT. SAMPO 90 High Resolution Interactive Gamma-Spectrum Analysis Including Automation with Macros. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 1992;160(1):289–295. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bevington PR. Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences. McGraw-Hill, Inc; New York: 1969. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Searle BC, Dasari S, Turner M, Reddy AP, Choi D, Wilmarth PA, McCormack AL, David LL, Nagalla SR. High-throughput identification of proteins and unanticipated sequence modifications using a mass-based alignment algorithm for MS/MS de novo sequencing results. Anal Chem. 2004;76(8):2220–30. doi: 10.1021/ac035258x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Takemoto L. Deamidation of Asn-143 of gamma S crystallin from protein aggregates of the human lens. Curr Eye Res. 2001;22(2):148–53. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.22.2.148.5524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Purkiss AG, Bateman OA, Goodfellow JM, Lubsen NH, Slingsby C. The X-ray crystal structure of human gamma S-crystallin C-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(6):4199–205. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110083200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yao X, Freas A, Ramirez J, Demirev PA, Fenselau C. Proteolytic 18O labeling for comparative proteomics: model studies with two serotypes of adenovirus. Anal Chem. 2001;73(13):2836–42. doi: 10.1021/ac001404c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sevinsky JR, Brown KJ, Cargile BJ, Bundy JL, Stephenson JL., Jr Minimizing back exchange in 18O/16O quantitative proteomics experiments by incorporation of immobilized trypsin into the initial digestion step. Anal Chem. 2007;79(5):2158–62. doi: 10.1021/ac0620819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.May D, Fitzgibbon M, Liu Y, Holzman T, Eng J, Kemp CJ, Whiteaker J, Paulovich A, McIntosh M. A platform for accurate mass and time analyses of mass spectrometry data. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(7):2685–94. doi: 10.1021/pr070146y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Faca V, Coram M, Phanstiel D, Glukhova V, Zhang Q, Fitzgibbon M, McIntosh M, Hanash S. Quantitative analysis of acrylamide labeled serum proteins by LC-MS/MS. J Proteome Res. 2006;5(8):2009–18. doi: 10.1021/pr060102+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Story board illustrating the MICIT workflow for handling multi-dimensional datasets is shown in Supplemental File 1. Algorithm pseudo code is listed in Supplemental File 2. SEQUEST peptide identification results from all LC/MS/MS experiments are available as a Scaffold file (version 2.0) upon request. A free version of Scaffold viewer can be downloaded from www.proteomesoftware.com. The software is available for non-commercial use from the authors upon written request via material transfer agreement with Oregon Health & Science University (Portland, OR).