Figure 4.
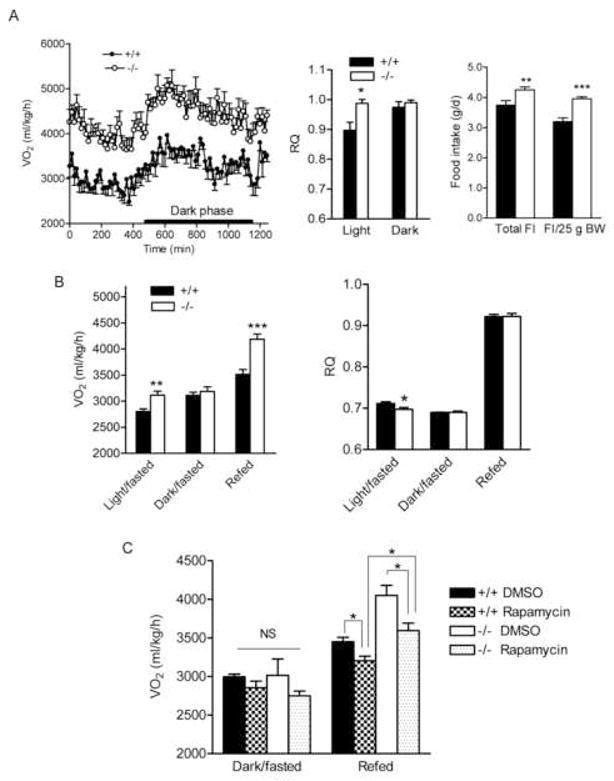
Elevated energy expenditure in BCATm null mice is associated with food consumption and is partially blunted by Rapamycin
A) Oxygen consumption (VO2, left panel), respiratory quotient (RQ, middle panel), and food intake (FI, right panel). Male mice fed a choice of amino acid purified BCAA-containing (+BCAA) and BCAA-free diet for 4 weeks were placed in indirect calorimetry chambers at the age of ~16 weeks. Food intake was measured for 3 weeks and calculated as average daily values. It was also adjusted for body weight (25g). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001, n=8.
B) VO2 (left panel) and RQ (right panel) during fasted-refed. Male mice fed a mix of NC and −BCAA diets were fasted for 21 h and refed with a choice of NC and BCAA diets. VO2 and RQ were measured during fasting (light and dark phases) and a 3-h refeeding period. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001, n=6.
C). VO2 after treated with rapamycin during fasted-refed. 12–15 week old mice were i.p. injected with 0.75 mg/kg of rapamycin at 11 a.m. and fasted for 21 h and injected again with the same dose of rapamycin. Food was provided 1-h after second injection for 3 h. VO2 was measured during the dark phase and refeeding. One way ANOVA was used to compare VO2 among groups under each nutritional condition. No difference was found between groups during fasting. * P < 0.05 between groups during refed, n=8–11.
