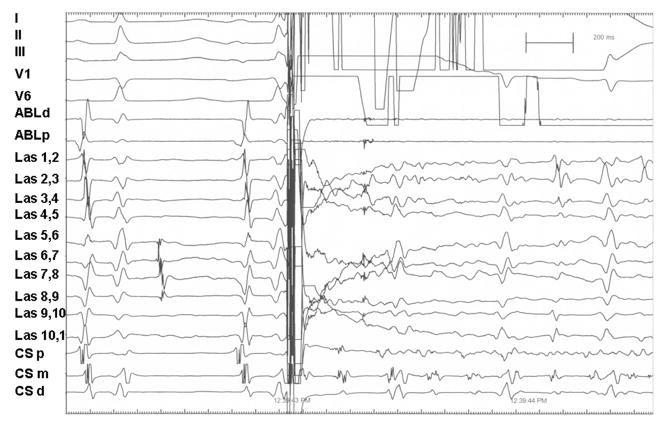
Figure 1.
External 30 J shock during sinus rhythm induces atrial fibrillation. During sinus rhythm a 30 J external biphasic shock synchronized to the R wave is delivered, which induces atrial fibrillation. Note the dissociated pulmonary vein electrogram seen on Lasso catheter poles 5–9 prior to the external shock, demonstrating successful exit and entrance block to this pulmonary vein. Surface leads I, II, III, V1, and V6 are shown as labeled. Intracardiac recordings from an 8 mm tip ablation catheter at the proximal and distal electrodes, 10 overlapping bipolar recordings from a circumferential catheter (Lasso 1–10) placed in the left inferior pulmonary vein, and bipolar recordings from the distal (CSd), mid- (CSm), and proximal (CSp) coronary sinus catheter are shown at a paper speed of 100 mm/sec.