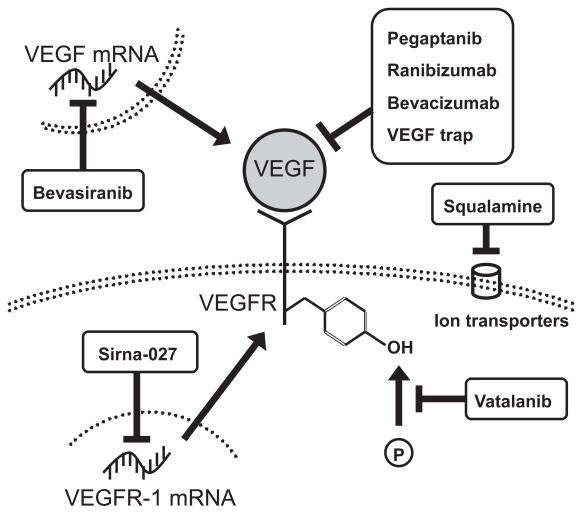
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF). Pegaptanib, ranibizumab, bevacizumab, and VEGF trap bind and sequester VEGF, preventing it from binding and activating VEGF receptor. Inhibitors of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases prevent transduction of the VEGF binding signal. Small interfering RNA molecules prevent translation of VEGF (bevasiranib) or VEGF receptor-1 (Sirna-027). Squalamine interferes with the function of various ion transport channels, the activity of which is required for angiogenesis. Double dotted lines represent cellular plasma membranes and the single dotted line represents nuclear membrane.