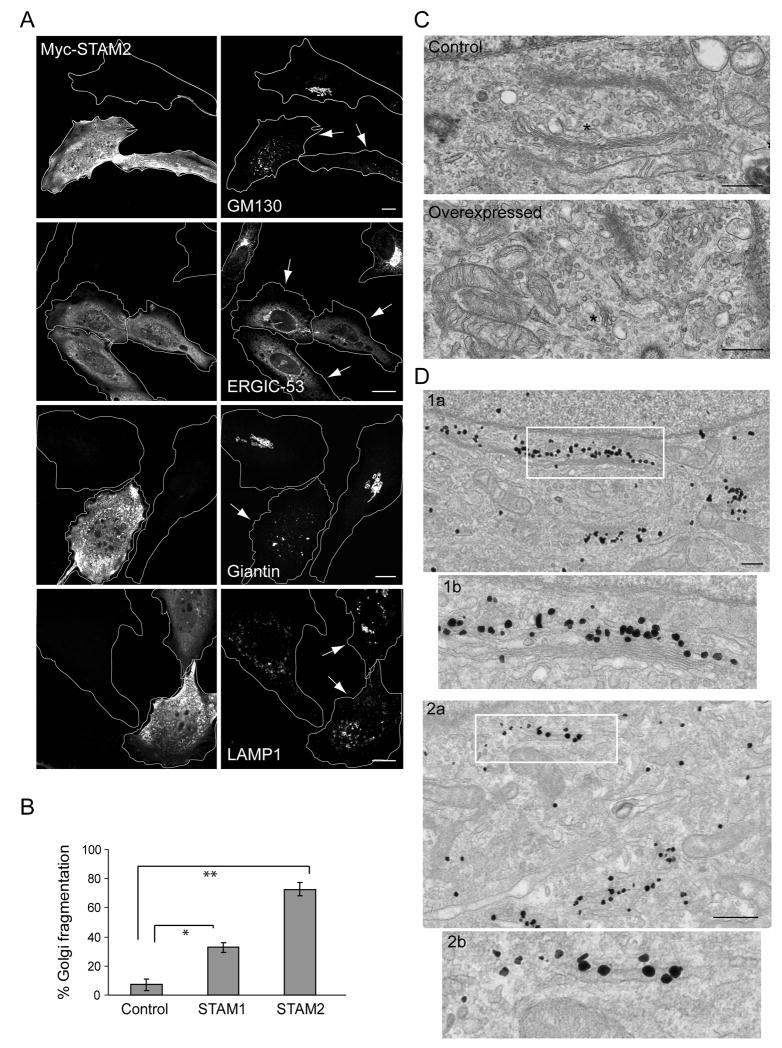
Figure 2. Overexpression of STAMs causes dispersion of the Golgi complex.
A) Overexpression of Myc-STAM2 (left panels) in HeLa cells disperses the Golgi markers GM130 and giantin, and causes ERGIC-53 to be retained in the ER, but does not affect LAMP1 distribution (right panels). Golgi apparatus and VTCs exhibit normal, perinuclear localization patterns in untransfected cells. Arrows identify transfected cells. Bar, 10 μm. B) Quantification of Golgi fragmentation in cells overexpressing Myc-STAM1, Myc-STAM2, or empty vector (Control) (n=3; 100 cells per experiment; ±SD). *p=0.0012; **p<0.001. C) Electron microscopy images showing typical Golgi morphology in control cells (asterisk; top panel), but much smaller stacked Golgi complexes in STAM2-overexpressing cells (asterisk; bottom panel). Images are at the same magnification. Bar, 500 nm. D) Immunogold localization of GM130 in control cells (1a), with higher magnification of the boxed area in (1b). Immunogold localization of GM130 in STAM2-overexpressing cells (2a), with the boxed region enlarged in (2b). Bar, 500 nm.