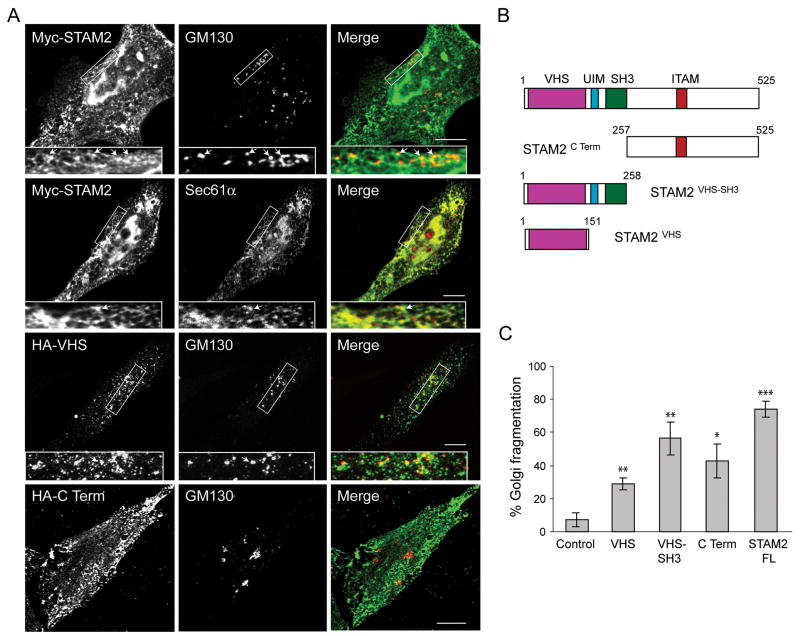
Figure 3. Effects of STAM2 deletions on subcellular distribution and Golgi fragmentation.
A) HeLa cells transfected with full-length Myc-STAM2, HA-STAM2VHS, or HA-STAM2C Term were treated with saponin to deplete cytosolic proteins and then co-stained for Myc- or HA-epitope and GM130 or, Sec61α. HeLa cells overexpressing full-length STAM2 or the C-terminal fragment display the lattice-like staining adjacent to GM130 puncta, with areas of juxtaposed staining indicated with arrows (upper panels). Colocalization of thhe Myc-STAM2 lattice-like staining with the ER protein Sec61α is shown in the middle panels. In cells expressing HA-tagged STAM2VHS, the juxtapositioned pattern with GM130 is more evident. Boxed areas are enlarged in the insets. B) Schematic diagram of STAM2 deletion constructs. Amino acid numbers are indicated. C) HeLa cells were transfected with control vector, HA-STAM2VHS, HA-STAM2VHS-SH3, HA-STAM2C Term, or full-length Myc-STAM2 (FL), co-stained with GM130 and either Myc- or HA-epitope antibodies, then assessed for Golgi fragmentation (100 cells per condition; n=3; ±SD). *p<0.01; **p<0.005; ***p<0.001.