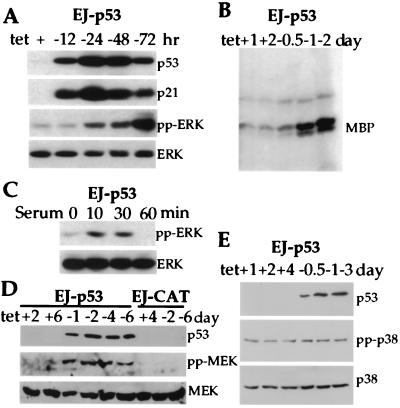
Figure 1.
Activation of MAPK/MEK pathway by inducible expression of p53. (A) Increased phosphorylation of ERK (pp-ERK) in response to wt p53 induction. EJ-p53 cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis for the induction of p53 protein with (+) or without (−) tet. The expression of p21, pp-ERK, and total ERK proteins was also monitored. (B) Enzymatic activity of ERK in EJ-p53 cells with (+) or without (−) tet. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-ERK antibody, and kinase activity was measured with myelin basic protein (MBP) as substrate. (C) Phosphorylation of ERK in response to serum stimulation. Starved EJ-p53 cells were stimulated with serum in the presence of tet. (D) Activation of MEK1 after p53 induction. Lysates from EJ-p53 cells grown with (+) or without (−) tet for different time periods were immunoblotted with anti-p53, anti-phospho-specific MEK1, and anti-MEK1 antibodies. (E) No change in active p38 and total p38 MAPK after p53 induction. Lysates from EJ-p53 cells grown with (+) tet or without (−) tet for different time periods were immunoblotted with anti-p53, anti-phospho-specific p38, and anti-p38 antibodies.