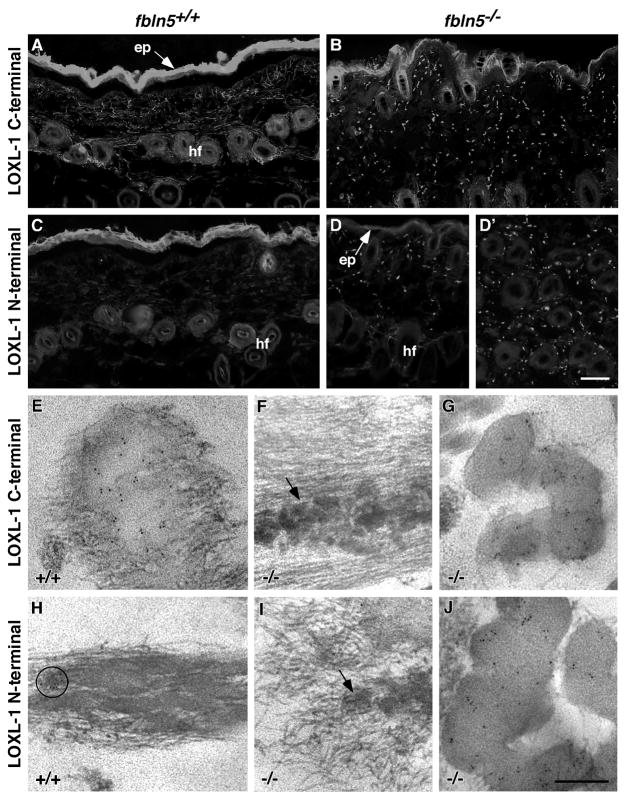
Figure 5. LOXL-1 localization in mouse skin.
Wild-type and Fbln5−/− skin sections were immunolabeled at the light and electron microscope levels using a C-terminal LOXL-1 antibody that recognizes both the active and inactive forms of LOXL-1 and an N-terminal LOXL-1 antibody that recognizes only the inactive form. Immunolabeling with the C-terminal antibody shows LOXL-1 staining in filamentous network between adjacent hair follicles (hf) and within the papillary dermis between the hair follicles and epidermis (ep) in wild-type skin (A) and a punctate staining pattern in the Fbln5−/− skin (B). Wild-type skin shows no immunostaining for the N-terminus of LOXL-1 in wild-type skin (C), whereas a punctate staining is observed in the Fbln5−/− skin, both between the epidermis (ep) and hair follicles (hf) (D) and deeper in the dermis between the individual hair follicles (D′). Immunofluorescence of the epidermis is non-specific. Immunogold electron microscopy using the C-terminal antibody shows gold particles on the edges of the elastin core of the elastic fibers and where the microfibrils were embedded within the core in wild-type skin (E). In Fbln5−/− skin, no labeling is seen on the small elastin globules (F), but considerable gold particles are seen to decorate the large elastin deposits (G). Only the occasional, rare patch of gold particles was seen on elastic fibers in wild-type skin for the N-terminus of LOXL-1 (H - circle). No immunogold labeling for the N-terminus of LOXL-1 was seen on the small elastin globules in the Fbln5−/− skin (I), however, abdundant gold particles localize to the larger elastin deposits (J). Scale bars = 100 μm (A–D), 0.3 μm (E–J).