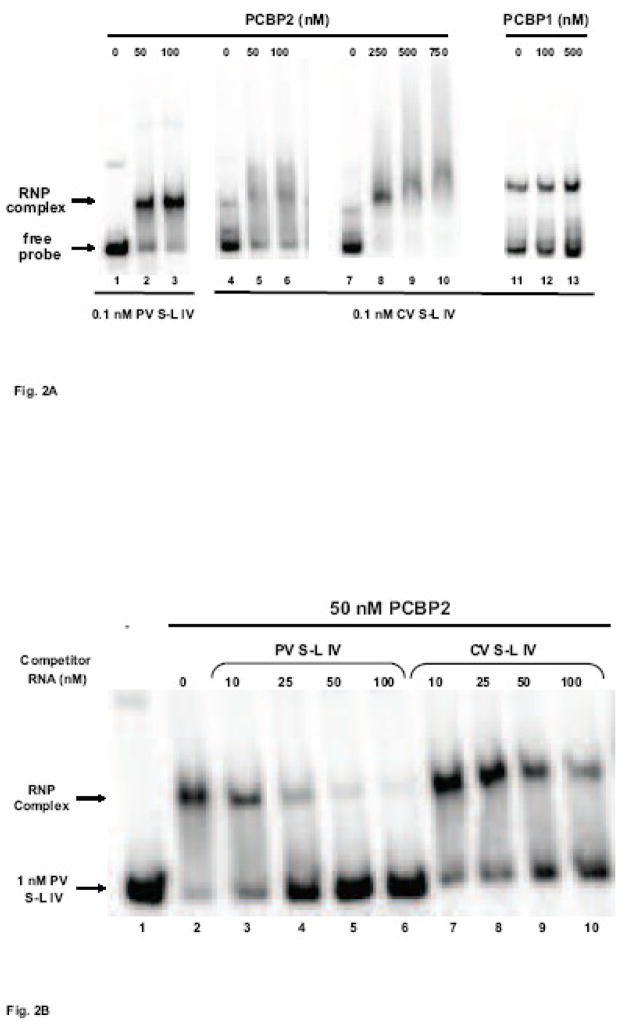
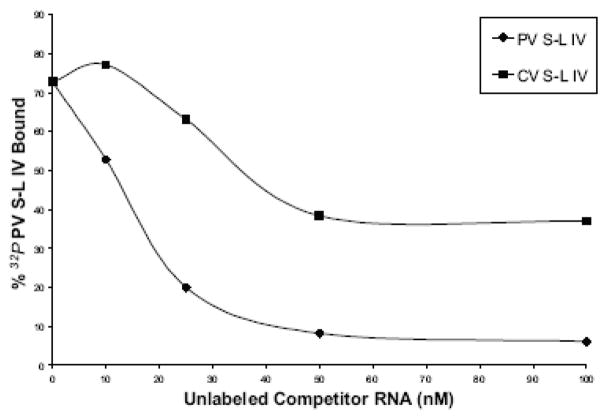
Figure 2. Mobility shift assays of coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA with PCBP2 and PCBP1.
A. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays of poliovirus and coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA with recombinant PCBP2 and PCBP1. In vitro transcribed, 32P-labeled stem-loop IV RNA at a final concentration of 0.1 nM was incubated with increasing amounts of purified recombinant PCBP2 for 10 min at 30°C, and the reaction was then subjected to native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Lanes 1, 4, 7, and 11 are the RNA alone. Poliovirus stem-loop IV RNA (lanes 2–3) and coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA (lanes 5–6 and 8–10) can form ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes with PCBP2. The RNP complex is denoted by the arrow. PCBP1 (lanes 12–13) is unable to interact with coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA. B. Competition electrophoretic mobility shift assay of poliovirus stem-loop IV RNA and PCBP2 using unlabeled coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA. In vitro transcribed 32P-labeled poliovirus stem-loop IV RNA (1 nM) was incubated with PCBP2 (50 nM) in the presence of increasing amounts of unlabeled poliovirus (lanes 3–6) or coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNAs (lanes 7–10) for 10 min at 30°C. The RNP complexes were then resolved on a native polyacrylamide gel. RNP complexes are denoted by the arrow. C. Graph of relative binding affinities of PCBP2 for poliovirus and coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA. The relative affinities of PCBP2 for the stem-loop IV RNAs were determined by measuring the band intensity of the bound RNA divided by the sum of the free RNA and bound RNA. It was observed that 15 nM unlabeled poliovirus stem-loop IV RNA was enough to dissociate half of the labeled poliovirus stem-loop IV-PCBP2 RNP complex, while it required 35 nM unlabeled coxsackievirus stem-loop IV RNA to obtain the same level of competition.