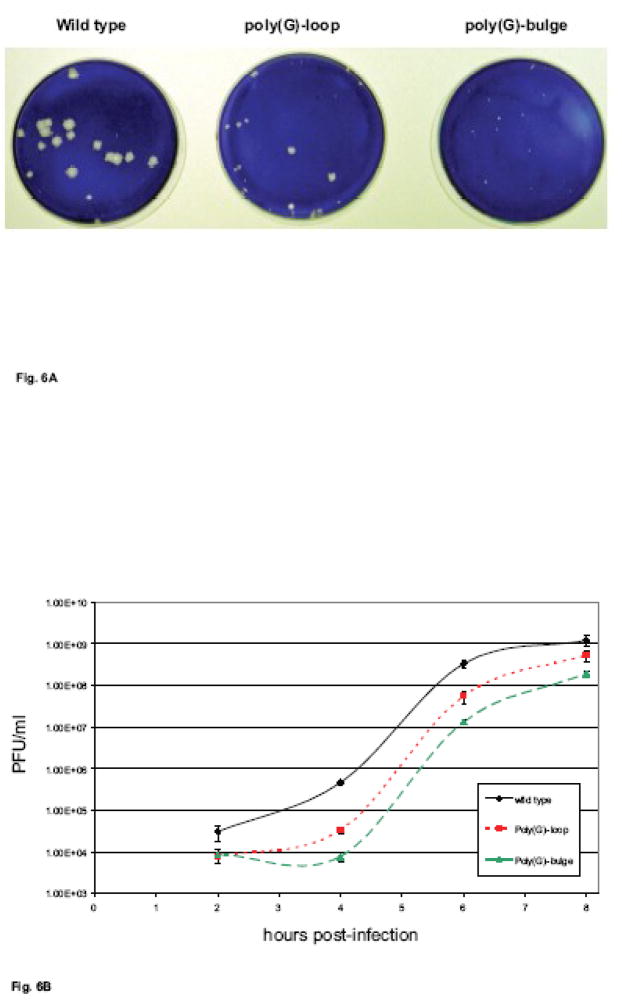
Figure 6. Growth properties of coxsackievirus mutants with poly(G) substitutions in stem-loop IV RNA.
A.Plaque size morphology. In vitro transcribed full-length wild type, poly(G)-loop, or poly(G)-bulge mutated stem-loop IV coxsackievirus RNAs were transfected into HeLa cell monolayers. Readily visible plaques formed at 3 days post-transfection. Wild type coxsackievirus RNA produced large plaques, while the poly(G) mutated stem-loop coxsackievirus RNAs produced smaller plaques. B. Single cycle growth analysis of coxsackievirus mutants with poly(rG) nucleotide substitutions in stem-loop IV. HeLa cell monolayers were infected with wild type -◆-, poly(G)-loop -■-, or poly(G)-bulge -▲-mutated coxsackieviruses at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10. The infected monolayers were harvested at the indicated times after infection and the virus titers were determined by plaque assay on HeLa cells as described in Material and Methods. The virus titers are reported as the log10 PFU (plaque forming units) per milliliter (ml).