|
Independent variables
|

|
age |
Hr |

|
time |
Hr |
|
Dependent variables
|
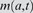
|
bone marrow cell age distribution |
cells/ml/hr |
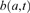
|
circulating RBC age distribution |
cells/ml/hr |
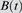
|
circulating RBC concentration |
cells/ml |
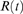
|
circulating reticulocyte concentration |
cells/ml |
|
Functions
|
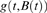
|
anaemia-induced fold-change in reticulocyte production rate over normal |
|
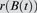
|
anaemia-induced fold-change in reticulocyte release rate over normal |
|
|
Parameters
|
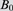
|
normal circulating RBC concentration, equal to 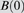
|
cells/ml |
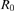
|
normal circulating reticulocyte concentration, equal to 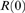
|
cells/ml |
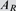
|
reticulocyte maturation time |
hr |
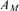
|
maximum residence time in bone marrow |
hr |
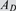
|
equal to 
|
hr |
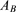
|
maximum RBC lifespan |
hr |

|
normal bone marrow reticulocyte release rate into circulation |
hr−1
|
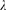
|
normal bone marrow reticulocyte production rate |
cell/ml/hr |

|
clearance rate of circulating RBCs |
hr−1
|

|
scaling factor between difference in normal and anaemic RBC concentrations and reticulocyte production rate |
(cells/ml)−1
|

|
maximum fold-change in reticulocyte production rate over normal |
|
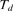
|
delay from PHZ treatment to increased reticulocyte production rate |
hr |

|
time lag in reticulocyte production rate |
hr |
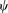
|
amplitude of oscillations of reticulocyte production rate |
|

|
initial phase of oscillations of reticulocyte production rate |
radians |
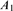
|
PHZ-induced change in age of RBCs of age 0 |
hr |
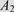
|
PHZ-induced change in age of RBCs of age 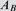
|
hr |
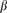 , , 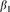
|
PHZ-induced RBC lysis rate |
hr−1
|
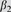
|
decay rate of PHZ |
hr−1
|
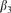
|
proportion of RBCs lysed just after PHZ treatment |
|

|
scaling factor between difference in normal and anaemic RBC concentrations and reticulocyte release rate |
(cells/ml)−1
|
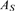
|
sampling-induced reticulocytes' maturation time |
hr |

|
fold-increase in sampling-induced reticulocytes' production over normal |
|
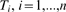
|
time when reticulocyte spike  starts starts |
hr |

|
duration of reticulocyte spike 
|
hr |

|
number of reticulocyte spikes |
|


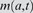
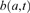
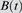
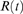
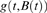
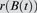
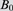
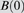
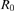
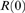
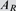
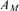
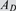

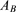

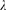



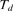

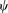

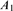
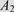
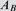
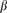 ,
, 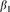
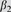
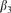

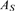

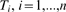
 starts
starts


