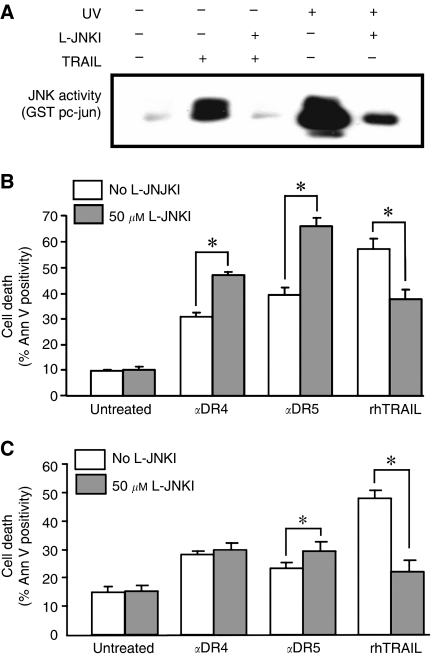
Figure 3.
Inhibition of JNK inhibits rhTRAIL-mediated apoptosis, but potentiates DR4- or DR5-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer cells. (A) L-JNKI can inhibit rhTRAIL-mediated JNK activation. HCT15 cells were preincubated for 1 h with L-JNKI (25 μM) followed by treatment with 50 ng ml−1 rhTRAIL for 3 h or UV for 30 min. The figure shows GST p-c-Jun phosphorylation by JNK as a measure of JNK activity. (B) Inhibition of L-JNKI potentiates apoptosis induced by selective activation of DR4 and DR5, but reduces apoptosis induced by rhTRAIL. Colo205 cells were treated for 3 h with either 20 ng ml−1 rhTRAIL or 5 nM of DR4/DR5 agonistic antibodies with or without 30 min pretreatment with L-JNKI (50 μM) and induction of apoptosis was measured with Annexin V. The graph shows average cell death±s.e.m. of four independent experiments. The asterisk (*) indicates significant differences (P<0.05). (C) Inhibition of L-JNKI potentiates apoptosis induced by selective activation of DR4 or DR5, but reduces apoptosis induced by rhTRAIL. HCT15 cells were treated for 3 h with either 50 ng ml−1 rhTRAIL or 10 nM of DR4/DR5 agonistic antibodies with or without 30 min pretreatment with L-JNKI (50 μM) and induction of apoptosis was measured with Annexin V. The graph shows average cell death±s.e.m. of three independent experiments. The asterisk (*) indicates significant differences (P<0.05).