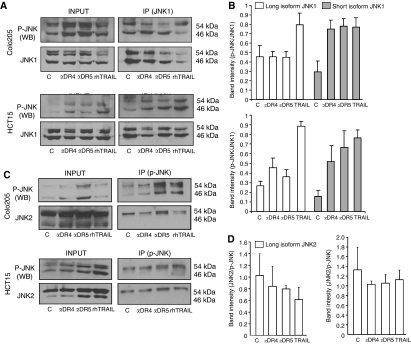
Figure 5.
rhTRAIL and selective activation of DR4 or DR5 leads to activation of distinct JNK1 isoforms. (A) Phosphorylation of JNK1 isoforms by rhTRAIL and agonistic DR4/5 antibodies. Colo205 cells were treated with 5 nM of agonistic DR4/5 antibodies or 20 ng ml−1 rhTRAIL. HCT15 cells treated with 10 nM of agonistic DR4/5 antibodies or 50 ng ml−1 rhTRAIL for 3 h. JNK1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and its phosphorylation pattern was assessed by western blotting with p-JNK antibody. JNK1 western blots show total JNK1 protein immunoprecipitated from cell lysates that was used for quantification of the amount of p-JNKI in the IP. (B) Densitometric quantification of p-JNK1 levels. The graph shows averaged p-JNK1 band densities normalised for total JNK1 levels in the immunoprecipitates of Colo205 (top) and HCT15 (bottom) cells from four independent experiments. (C) Phosphorylation of JNK2 isoforms by rhTRAIL and agonistic DR4/5 antibodies. Colo205 and HCT15 cells were treated as in point A and p-JNK protein (both JNK1 and 2) was immunoprecipitated. JNK2 phosphorylation was assessed in the p-JNK immunoprecipitates by probing the blots with a JNK2-specific antibody. P-JNK protein levels were also determined for quantification of JNK2 phosphorylation. (D) Densitometric quantification of p-JNK2 levels in Colo205 (left) and HCT15 (right) cells. The graph shows averaged p-JNK2 band densities normalised for total JNK2 levels in the immunoprecipitates from two independent experiments.