Figure 2. Acetylation of the ERα and AR are regulated by both TSA and NAD sensitive histone deacetylases.
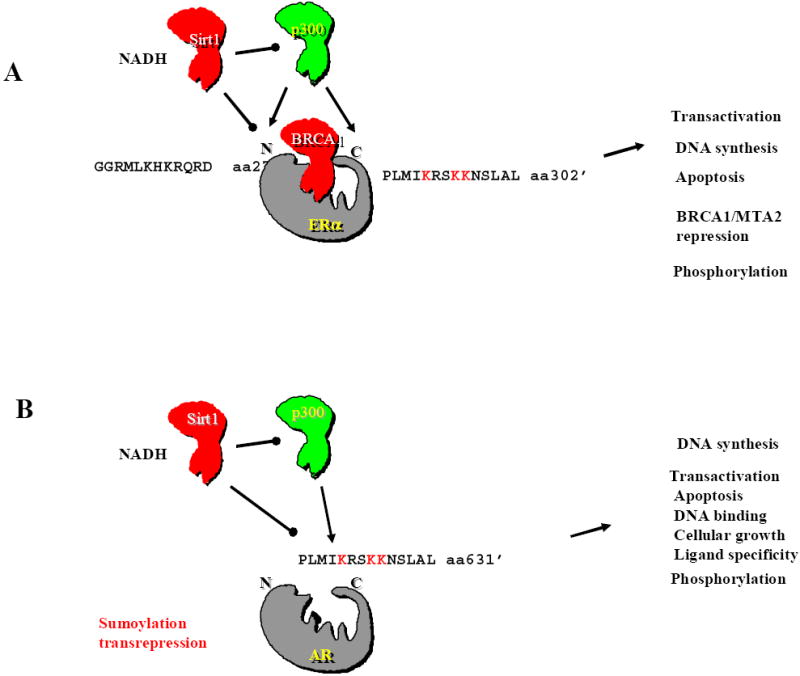
ERα and AR share conserved lysine residues that are acetylated by distinct HATs (reproduced with permission from (55)). The ERα is shown associated with the BRCA1 protein, which is known to repress activity of the ERα (56, 57). The two known acetylation sites of the ERα and their amino acid sequence is shown. p300 is a coactivator of the ERα and the AR. SIRT1 is known to deacetylate and thereby repress the activity of p300 (13). The ERα may be a target of SIRT1 as chemical inhibitors of SIRT1 regulate ERα activity. The acetylation site of the ERα has been shown to govern several functions (29) (transactivation, DNA synthesis, apoptosis, BRCA1 repression). (B)The AR acetylation site is shown as a substrate for p300 acetylation and for deacetylation by SIRT1-Acetylation of the AR has been shown to regulate several key functions of the AR (DNA synthesis, transactivation, and cellular growth (35, 37, 39, 58) but does not affect AR-mediated transrepression or sumoylation.
