Figure 1.
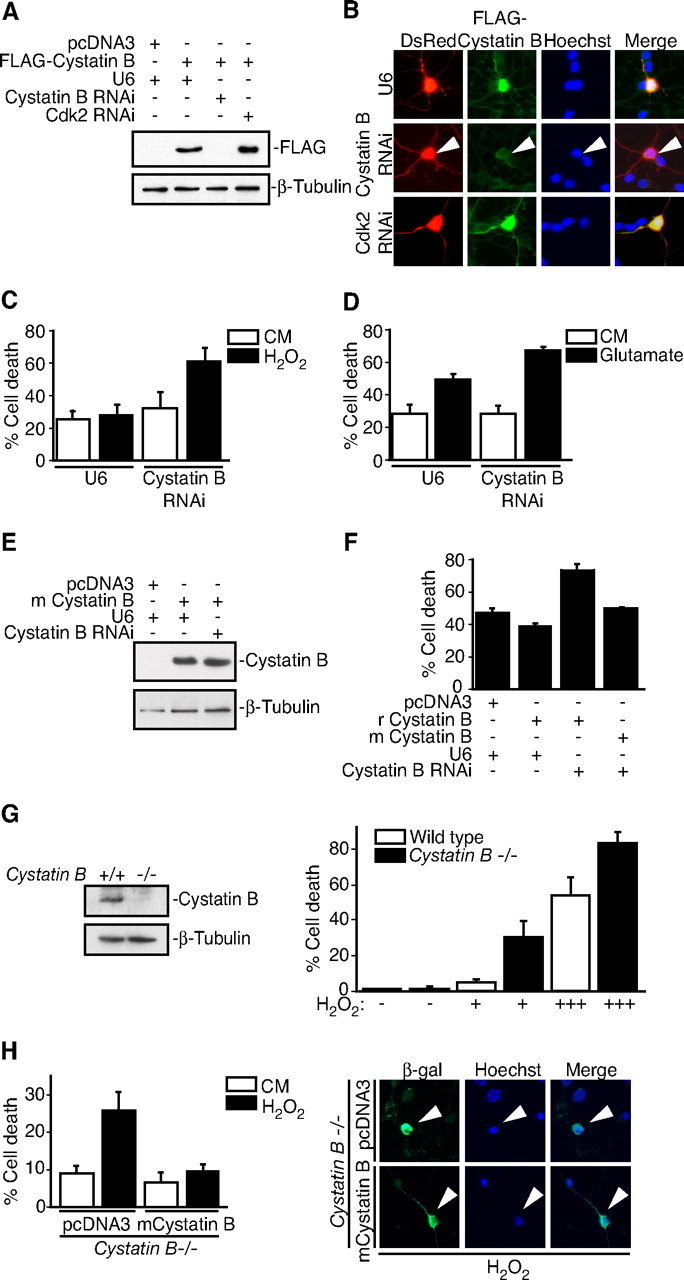
Cystatin B deficiency sensitizes neurons to oxidative stress. A, Lysates of 293T cells transfected with the rat FLAG—Cystatin B expression vector or control plasmid together with the Cystatin B hpRNA, Cdk2 hpRNA, or control U6 plasmid were immunoblotted with the Cystatin B and β-tubulin antibodies. B, Immunocytochemical analysis of rat granule neurons transfected with FLAG—Cystatin B and DsRed expression plasmids together with the Cystatin B hpRNA, Cdk2 hpRNA, or control U6 plasmid. Cystatin B RNAi reduced FLAG–Cystatin B expression in an average of 63.2% of transfected cells (n = 2). C, Rat granule neurons were transfected with the Cystatin B hpRNA or control U6 plasmid together with the β-galactosidase expression plasmid. After 72 h, cultures were treated with H2O2 for 24 h. Percentage cell death in transfected β-galactosidase-positive neurons is represented as mean ± SEM. Cystatin B knockdown sensitized neurons to H2O2-induced cell death (ANOVA; p < 0.05; n = 3). D, Rat granule neurons transfected with the Cystatin B hpRNA or control U6 plasmid together with the β-galactosidase expression plasmid were treated with 10 mm glutamate for 24 h and analyzed as in Figure 1C. Cystatin B RNAi sensitized neurons to glutamate-induced cell death (ANOVA; p < 0.05; n = 3). E, Lysates of 293T cells transfected with the mouse (m) Cystatin B expression vector or control plasmid together with the Cystatin B hpRNA or control U6 plasmid were immunoblotted with the Cystatin B and β-tubulin antibodies. F, Rat granule neurons transfected with the rat (r)FLAG–Cystatin B or mCystatin B expression plasmid and the β-galactosidase expression vector together with the Cystatin B RNAi plasmid were treated with H2O2 and analyzed as in C. Mouse Cystatin B rescued neurons from rat Cystatin B RNAi sensitization to H2O2-induced death (ANOVA; p < 0.001; n = 3). G, Left panels, Lysates of wildtype and Cystatin B−/− mouse granule neurons were immunoblotted with the Cystatin B or β-tubulin antibodies. Right panels, Cultures of Cystatin B−/− and wild-type control granule neurons were treated with increasing amounts of H2O2 and analyzed as in C. Cell death significantly increased in Cystatin B−/− neurons during H2O2 treatment compared with control (ANOVA; p < 0.0001; n = 3). H, Left panels, Cystatin B−/− granule neurons transfected with the mouse Cystatin B or control plasmid together with the β-galactosidase expression plasmid were treated with H2O2 and analyzed as in C. Cystatin B expression in Cystatin B−/− neurons rescued neurons from oxidative stress sensitivity (ANOVA; p < 0.01; n = 3). Right panels, Arrowheads denote representative images of neurons scored for survival.
