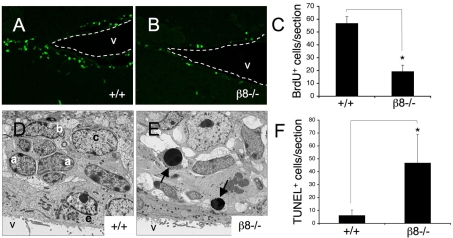
Fig. 6.
Neural cell proliferation and survival defects in the β8–/– subventricular zone. (A,B) Sagittal brain sections from P60 wild-type (A) and β8–/– (B) mice that were killed after receiving intraperitoneal injections of BrdU, were immunofluorescently labeled with anti-BrdU antibody. Dashed white lines denote ventricle boundaries. (C) Brain sections from wild-type (n=6) and β8–/– (n=11) mice were immunofluorescently labeled with anti-BrdU antibody and BrdU+ cells were quantified by analyzing serial sections. Note the significant reduction in the numbers of proliferating cells in the SVZ of β8–/– mutant mice, *P<0.001 compared with wild-type samples. (D,E) Ultrastructural analyses of SVZ regions dissected from P90 wild-type (D) and β8–/– (E) mice. Unlike the wild-type SVZ (D), which contains distinct units of a, b and c cells, the SVZ in β8–/– mice has an abnormal cytoarchitecture with increased numbers of apoptotic cells (arrows in E). (F) Serial coronal sections through the SVZ of P60 wild-type (n=7) and β8–/– (n=9) mice were immunofluorescently labeled to identify TUNEL+ cells and these cells were quantified. Note the higher numbers of apoptotic cells in the SVZ of β8–/– mice. *P<0.001 compared with wild-type samples. V, ventricle; BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; a, SVZ type a neuroblast; b, SVZ neural stem cell; c, SVZ transit amplifying cell.