Figure 2.
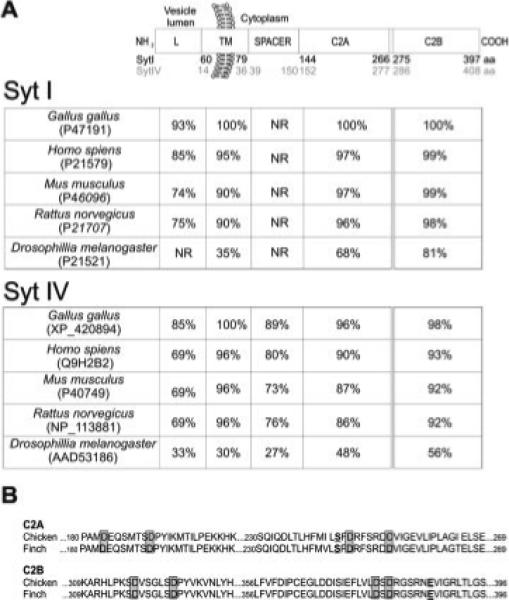
Domain structure and percent identity of zebra finch Syt I and Syt IV orthologs. (A) Top schematic highlights the Syt I and Syt IV functional domains. Approximate amino acid (aa) boundaries in the deduced zebra finch sequences are indicated for the luminal (L), transmembrane region (TM), spacer region (SPACER) and the two C2 calcium-binding domains (C2A and C2B) of Syt I (black) and Syt IV (gray). Beneath, two tables show the percent amino acid identity of zebra finch Syt I or Syt IV to corresponding sequences of chicken, mammals and fruit fly with GenBank accession numbers indicated. The range of residues that comprise the spacer region of Syt I has not been reported for mammalian and fly orthologs (NR). (B) Alignment of portions of the avian C2A and C2B domains highlights the conserved aspartate residues (gray boxes) thought to coordinate calcium binding. The amino acid substitution (Asp → Ser) characteristic of the Syt IV C2A domain is bolded and underlined. Within the C2B domain, a conservative substitution (Glu → Asp) occurs at position 386 that is thus far unique to avian sequences.
