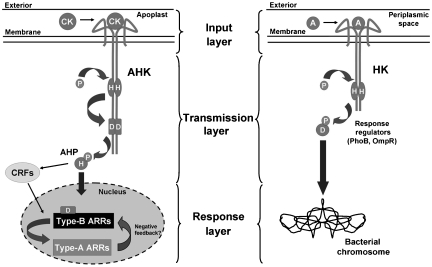
Figure 1.
Comparison of HK signal transduction systems from plants and bacteria. Ligands bind to the extracellular domain of transmembrane HKs and activate a cytoplasmic kinase domain. A phospho-relay (His → Asp in bacteria or His → Asp → His → Asp in plants) transmits the signal to DNA. Both systems can be defined as perceiving an input stimulus (input layer), transmitting the signal (transmission layer), and bringing about a response (response layer), but use different numbers of components. In simple bacterial systems (right panel), two proteins (HK and RRs) function in three layers. In plants (left panel), cytokinin responses involve multiple components that are each encoded by multigene families in these three layers. AHK, arabidopsis histidine kinase; AHP, arabidopsis histidine phosphotransfer protein; CK, cytokinin; HK, histidine kinase; H, histidine residue; D, aspartate residue; P, phosphate group; CRF, cytokinin response factor; ARR, Arabidopsis response regulator; A, bacterial HK ligand.