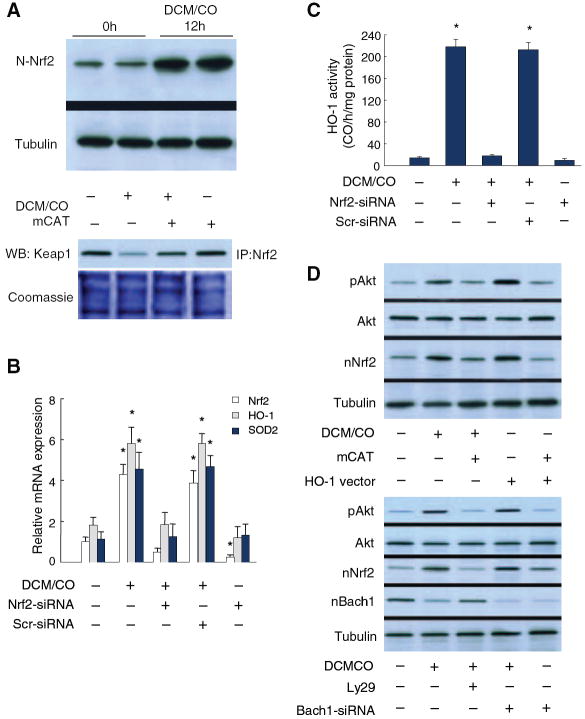
Figure 2.
Nrf2 expression in mouse cardiomyocytes. HL-1 cells exposed to DCM/CO (50 μmol/L) increase nuclear Nrf2 content by >5-fold along with cytoplasmic Keap1 dissociation that is blocked by mitochondrial-targeted catalase (mCAT) (A). B, DCM/CO increases Nrf2, HO-1, and SOD2 mRNA levels by 3- to 4-fold, whereas Nrf2 silencing abrogates the mRNA responses and scrambled siRNA has no effect. *P<0.05 compared with control (n=4). C, DCM/CO increases HO-1 enzyme activity by >10-fold, also abrogated by Nrf2 silencing but not by scrambled siRNA. *P<0.05 (n=4). D, Top, HL-1 cells treated with DCM/CO (50 μmol/L) or overexpressing HO-1 increase Akt phosphorylation and nuclear Nrf2 accumulation. mCAT inhibits HO-1-induced Akt activation and Nrf2 nuclear translocation. D, Bottom, PI3-kinase inhibition shows Akt primarily regulates Nrf2 translocation, not exclusion of the Bach1 nuclear repressor. DCM/CO produces greater Akt activity but less nuclear Bach1, whereas Akt inhibition does not affect nuclear Bach1 but reduces Nrf2 translocation. Bach1 siRNA increases nuclear Nrf2 with stable Akt activity.