Figure 4.
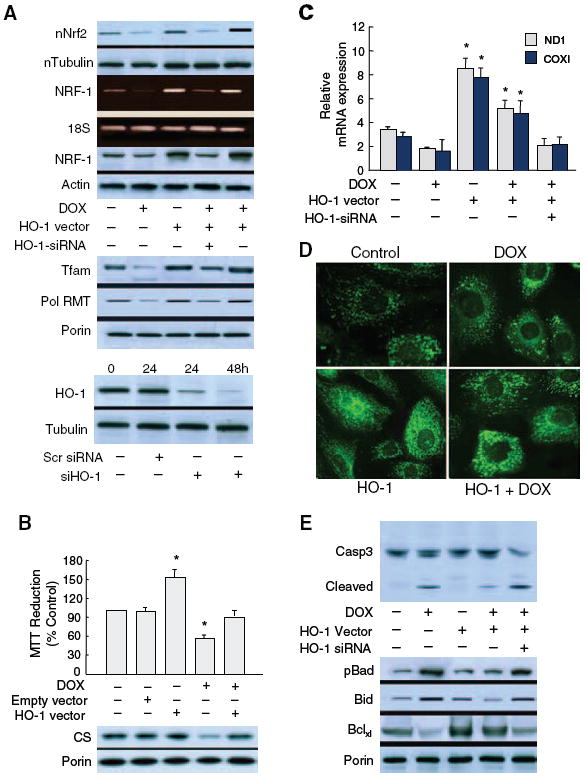
Nrf2/HO-1 induction of NRF-1 activates mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Nuclear Nrf2 and NRF-1 expression were evaluated in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts without and with HO-1 overexpression or silencing compared with readouts of 2 nuclear-encoded downstream genes, Tfam and PolRMT, that regulate mitochondrial mRNA levels and with which Dox interferes (A, top). HO-1 overexpression doubles mitochondrial Tfam and PolRMT protein and attenuates Dox interference (A, middle). A, Bottom, demonstrates effective HO-1 silencing at 24 and 48 hours. Mitochondrial functional protection by HO-1 is reflected by enhanced MTT reduction and citrate synthase (CS) expression (B) and mRNA for mitochondrial-encoded subunits COX I and ND1 (C). Dox-induced changes in Mitotracker green show organelle modification from a fine reticulum to vesicles and aggregates within 24 hours (D, top). In contrast, mitochondrial density in cells overexpressing HO-1 is greater than control, and changes in mitochondrial structure occur sporadically after Dox (D, bottom). E, Dox-induced caspase 3 cleavage; HO-1 overexpression limits and HO-1 silencing exacerbates caspase 3 cleavage. Dox also decreases mitochondrial Bcl-XL and increases mitochondrial phosphorylated Bad (Ser-112) protein, which is counteracted by HO-1 overexpression. HO-1 silencing reverses the effects of HO-1 expression on mitochondrial pBad, Bid, and Bcl-XL.
