Figure 5.
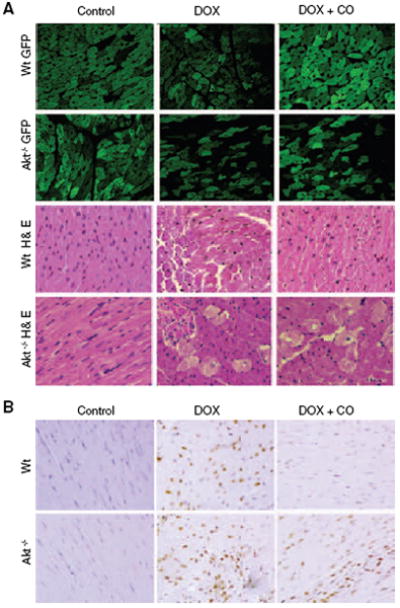
HO-1/CO, mitochondrial biogenesis, and cardiomyocyte survival. Mitochondrial damage and cell loss after Dox is more severe in Akt1−/− mice expressing mitochondrial GFP (Akt1−/−/GFP) than in Wt mice (A), and CO protects mitochondria and rescues cells in Wt but not Akt1−/− mice. Left ventricular myocardial sections stained with hematoxylin/eosin show interstitial edema, focal necrosis, and myofibrillar degeneration 7 days after Dox. Damage is more extensive in Akt−/− than Wt mice and ameliorated by CO in Wt but not Akt1−/− mice. B, TUNEL staining of heart sections from Wt and Akt1−/− mice before and 7 days after Dox. Large numbers of TUNEL-stained nuclei are noted after Dox, and CO protection is limited to the Wt. Supplemental Figure I shows the quantification of cardiac mitochondrial fluorescence in the GFP mice.
