Figure 4.
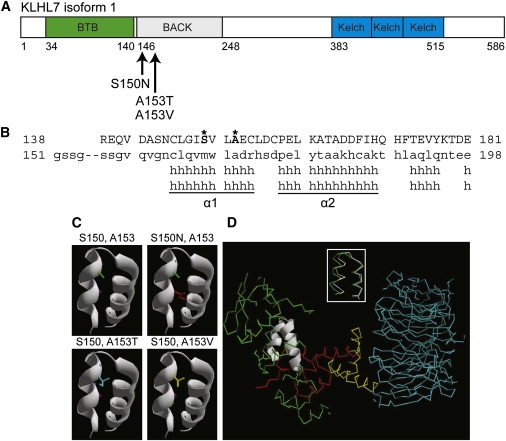
KLHL7 Protein Structure and Analysis
(A) Schematic of KLHL7 isoform 1. Mutations, reported here, are indicated.
(B) Protein alignment of the KLHL7 BACK domain to Kbtbd4. Mutant residues S150 and A153 are shown in bold and marked with an asterisk.
(C) Helical model of the KLHL7 BACK domain. S150 and A153 side chains are purple and green, respectively. Mutations 150N, 153T, and 153V are red, blue, and yellow, respectively. Each mutant side chain appears to occupy more space than the respective wild-type side chain in the cleft between two helices.
(D) Superimposition of α1 and α2 helices of the KLHL7 BACK domain on the Skp1 complex. The α1 and α2 helices of the KLHL7 BACK domain are structurally similar (RMSD = 0.84Å) to the α5 and α6 helices of Skp1 (inset). Green indicates Skp1. White is used to show an overlay of the BACK-domain α1 and α2 to α5 and α6 helices of Skp1. Red indicates the F box. Yellow indicates the helical linker. Blue indicates the WD40 domain. PDB:1nex.
