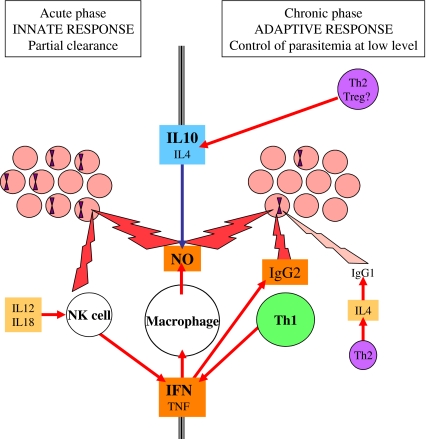
Figure 2.
Effector immune mechanisms and their regulation developed by the vertebrate during B. bovis infection. NO secreted by IFNγ-activated macrophages is the major effector mechanism against iRBC. During the acute phase, the innate response regulated by inflammatory and type-1 cytokines leads to partial elimination of the parasites injected by the tick. During the chronic phases, Th-1 cells and antibodies control parasitemia at a low level. IL4 and IL10 secreted by Th-2 or regulatory cells inhibit the activation of macrophages.