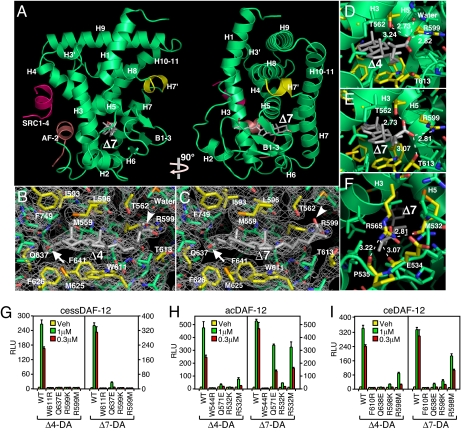
Fig. 3.
X-ray crystal structure of DAF-12 ligand-binding domain. (A) Ribbon model reveals the overall architecture of the ssDAF-12 ligand-binding domain (green) complexed with Δ7-DA (gray) and the SRC1 coactivator peptide (red). The AF-2 helix is shown in pink. (B and C) Electron density maps of the ssDAF-12 ligand binding pocket bound to Δ4-DA (B) or Δ7-DA (C). Carboxyls (arrowheads) and 3-ketos (arrows) of DA are shown. (D and E) H-bonding of ssDAF-12 aa directly involved in binding the C27-carboxyl group of Δ4-DA (D) or Δ7-DA (E). (F) The “lid” of the ligand binding pocket is formed by H-bond clamping between yellow-colored side-chain (R565) and main-chain oxygen atoms of M532, E534, and P535. H-bonds are illustrated by white dashed lines with bond lengths noted in Å. (G–I) Site-directed mutagenesis reveals differential ligand binding mechanisms for ssDAF-12 (G), acDAF-12 (H), and ceDAF-12 (I). Cotransfection assays were performed in CV-1 cells with the indicated receptors and a DAF-12 responsive reporter gene as in Fig. 2D. n = 3 ± SD.