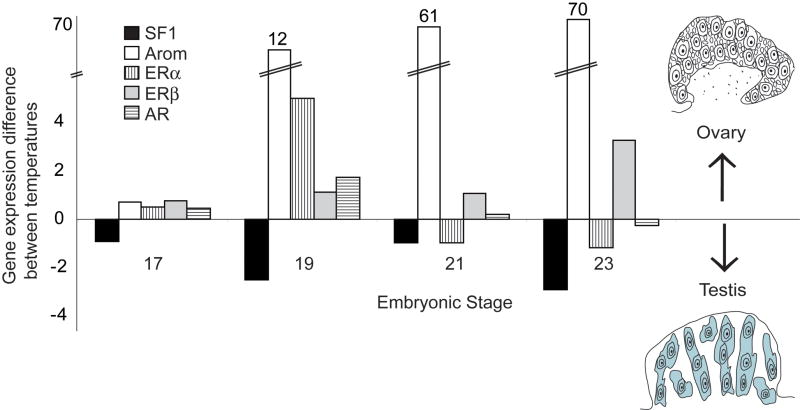
Figure 3.
Expression of components of the steroid signaling network is differential by temperature across development in the red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta). Steroidogenic factor 1 (Sf1), aromatase, estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), and androgen receptor (AR) expression levels within the gonad were measured with real-time qPCR, and the normalized expression levels for a male-producing temperature (26° C) were subtracted from female-producing temperature (31° C) values. For each gene, expression was calibrated to female expression levels at Stage 17, and then male expression values were subtracted from the female expression values for each stage. Gene expression levels higher at the female-producing temperature are therefore positive values, while levels higher at male-producing temperature are negative. Aromatase expression is dramatically higher than the other genes at FPT, and the Y-axis is scaled to reflect this (calibrated aromatase value given in parentheses at the top of the bar).