Fig. 1.
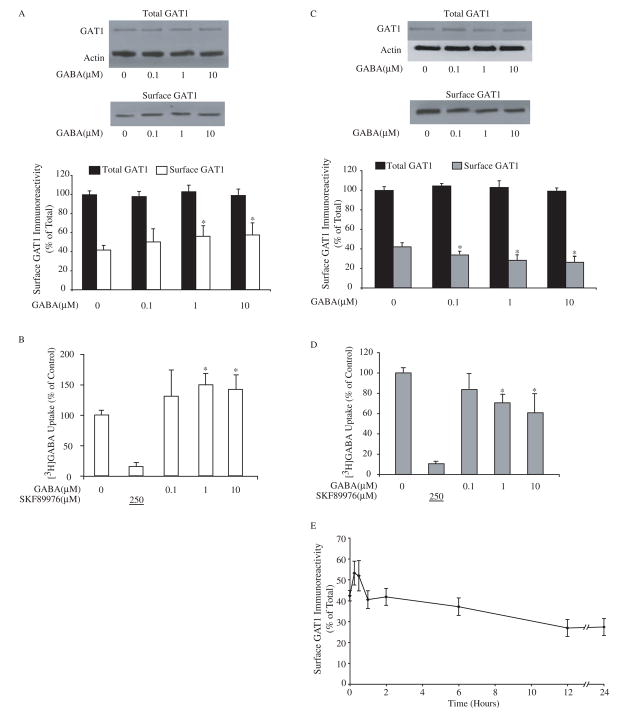
Extracellular GABA regulates the function of GABA transporter GAT1. A, short-term exposure to exogenous GABA increases surface expression of GAT1. Dissociated cortical neuron cultures were pre-treated with different concentrations of GABA for 30 min at 37 °C before surface biotinylation at 4 °C. Immunoblots show GAT1 and actin immunoreactivity in 0.2 volume of total cell lysate (upper panel) and GAT1 immunoreactivity in one volume of surface fraction (lower panel). The histogram illustrates the quantified results from eight experiments for surface GAT1 (white bar) and total GAT1 immunoreactivity (relative to actin, black bar). Surface GAT1 in the experimental conditions (white bars) that were significantly different from the control are denoted by the asterisk (p < 0.05). B, GABA uptake through GAT1 increases after short-term exposure to exogenous GABA. Cortical neuron cultures were pre-incubated in medium containing different concentrations of GABA for 30 min at 37 °C prior to uptake assay. Drug concentrations (in μM) are shown below the abscissa; the value underlined indicates that the drug was added only during the assay. Data are from five experiments, four wells/condition/experiment. GABA uptake under control conditions was 308 ± 121 fmol/min/mg of protein. GABA uptake that was significantly different from the control is denoted by the asterisk (p < 0.05). C, long-term GABA treatment decreases the surface expression of GAT1. Different concentrations of GABA were applied in culture medium for 24 hr at 37 °C before surface biotinylation. Immunoblots show GAT1 and actin immunoreactivity in 0.1 volume of total cell lysate (upper panel) and GAT1 immunoreactivity in one volume of surface fraction (lower panel). Data are from ten experiments and symbols are presented as in A. D, GABA uptake through GAT1 decreases after long-term exposure to exogenous GABA. Cortical neuron cultures were pre-incubated in medium containing different concentrations of GABA for 24 hr at 37 °C prior to uptake assay. Data are from five experiments, four wells/condition/experiment, and symbols are presented as in B. GABA uptake under control conditions was 315 ± 104 fmol/min/mg of protein. E, time-dependent changes in GAT1 surface expression due to GABA treatment. Dissociated cortical neurons were incubated in culture medium containing 10 μM GABA at 37 °C for different time periods prior to surface biotinylation at 4 °C. The time periods during which GABA was present in the medium are indicated on the abscissa. Data are from six separate experiments.