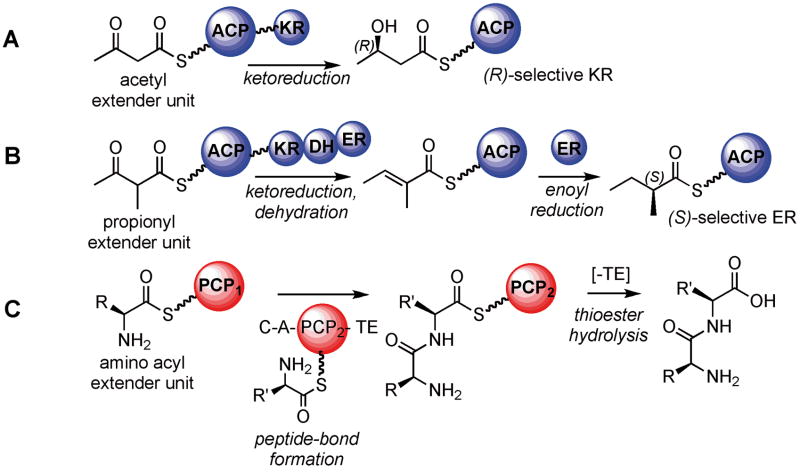
Figure 2.
Simplified schematics illustrating a few of the reactions catalyzed by megasynthase domains. A. KR domains use NADPH to reduce carbonyl groups to alcohols; exemplified here by an acetyl extender unit (malonyl group). Altering the stereoselectivity of KR domains could alter the product outcome. B. After KR and DH domain action on a propionyl extender unit (methyl-malonyl group), the resulting olefin can be reduced with NADPH by the action of stereoselective ER domains. Reengineering the ER stereoselectivity is also a potential means to alter product outcome. C. Illustration of NRPS domain actions on an amino acyl extender unit. A typical module is minimally composed of A (loading an amino acid onto the PCP domain), C (catalyzing the peptide bond formation), and PCP (carrying the amino acyl chain). The TE domain hydrolyzes the thioester linkage to release the natural product. KR: ketoreductase; DH: dehydratase; ER: enoyl-reductase; A: adenylation domain; C: condensation domain; PCP: peptidyl carrier protein domain; TE: thioesterase domain.