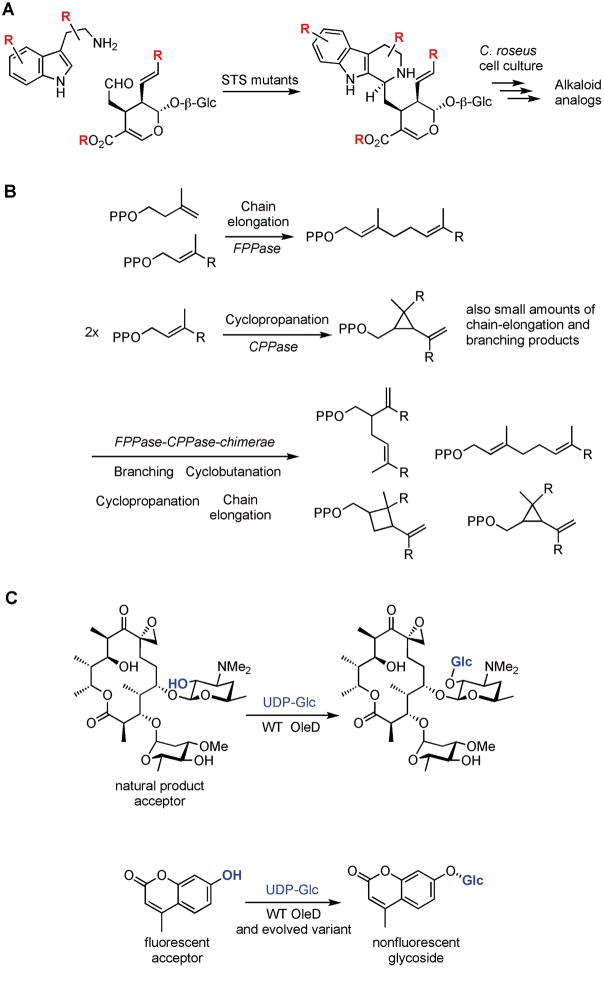
Figure 3.
Examples of enzyme engineering work on dissociated pathways. A. Strictosidine synthase (STS) catalyzes the Pictet-Spengler reaction between tryptamine and secologanin. STS variants, found by screening site-directed and saturation mutagenesis libraries, accept substrates not accepted by wild-type STS. B. Isoprenoids are synthesized by four coupling reactions: chain elongation, branching, cyclopropanation, and cyclobutanation. By replacing the sequences of a chain-elongating enzyme with the corresponding homologous sequences of a cyclopropanation enzyme, all four coupling reactions were observed. C. OleD catalyzes the C-O bond formation between the C-2 hydroxyl group on oleandomycin (acceptor) and the anomeric carbon of UDP-glucose (donor). OleD is 300-fold less efficient in transferring UDP-glucose onto 4-methylumbelliferone, a fluorescent surrogate substrate. Variants of OleD with enhanced activity were found by mutagenesis and screening the libraries in spectrophotometric assays for the loss of fluorescence of the acceptor starting material.