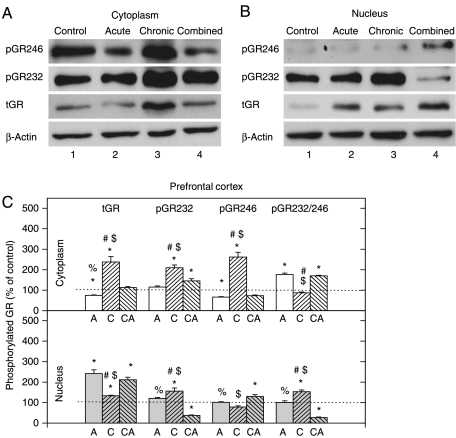
Figure 5.
Western-blot (WB) experiment demonstrating the effects of acute immobilization (A), chronic isolation (C), or combined stress (CA) on the levels of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and its phosphoisoforms in the cytoplasm and nucleus of prefrontal cortex: (A and B) GR phosphorylated at S246 (pGR246) or S232 (pGR232). Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with antibodies against total GR (tGR), pGR246, pGR232, or actin as a loading control. (C) Immunoreactivities of the cytoplasmic and nuclear GR, pGR232, and pGR246 (normalized to actin) and ratio of pGR232/pGR246 (normalized to GR in each compartment) are expressed as mean±s.e.m. (as described under Materials and Methods); n=15 animals per experimental group. Asterisks indicate significant differences between treated groups. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey's post hoc test and labelled as in Fig. 1.