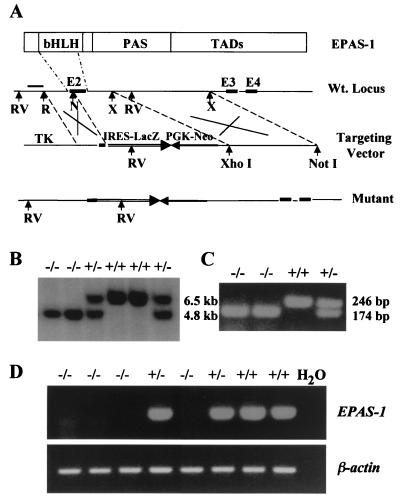
Figure 1.
Targeting of the EPAS-1 gene. (A) Targeting construct. A 1.9-kb EcoRI (R)/NaeI (N) fragment was used as the 5′ arm and a 6.2-kb XmnI (X) fragment as the 3′ arm. Homologous recombination results in the replacement of most of exon 2 (E2) and a region of intron after it (≈ 1.0 kb) by IRES-lacZ and PGK-Neo sequences. EcoRV (RV) digestion generates a 6.5-kb fragment for the wild-type allele and a 4.8-kb fragment for the targeted allele, both of which hybridize with the external probe (bar). (B) A Southern blot of DNA samples from embryos resulting from heterozygotes mating. (C) Genotyping by PCR. (D) Reverse transcription–PCR analysis of total RNA of E11.5 embryos for the expression of EPAS-1. The amount of template used and PCR efficiency for each reaction was normalized by reverse transcription–PCR for β-actin.